Content Menu
● Understanding Green Tea Extract
>> Key Components of Green Tea Extract
● Mechanisms of Appetite Suppression
● Scientific Evidence Supporting Appetite Suppression
>> Additional Research Findings
● Practical Implications for Weight Management
>> Delicious Ways to Incorporate Green Tea
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. How much green tea should I drink for appetite suppression?
>> 2. Are there any side effects associated with green tea extract?
>> 3. Can I rely solely on green tea extract for weight loss?
>> 4. Is there a difference between drinking green tea and taking extracts?
>> 5. Can anyone take green tea extract?
● Citations:
Green tea has long been celebrated for its health benefits, particularly in relation to weight management. Among its various properties, one of the most intriguing is its potential to suppress appetite. This article delves into the mechanisms behind this effect, the scientific evidence supporting it, and practical implications for those looking to manage their weight.

Understanding Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract is derived from the leaves of the *Camellia sinensis* plant and is rich in antioxidants called catechins, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). These compounds are believed to play a significant role in weight management and appetite suppression.
Key Components of Green Tea Extract
- Caffeine: A known stimulant that can enhance metabolism and fat oxidation.
- Catechins: Particularly EGCG, which may inhibit enzymes that break down norepinephrine, a hormone that promotes fat breakdown.
- Polyphenols: These compounds can influence various metabolic processes, including appetite regulation.
Mechanisms of Appetite Suppression
Research suggests several mechanisms through which green tea extract may suppress appetite:
1. Hormonal Regulation: Green tea can increase levels of cholecystokinin (CCK), a hormone released after eating that signals fullness to the brain. Higher CCK levels can lead to reduced hunger and lower food intake.
2. Inhibition of Appetite Hormones: The catechins in green tea may inhibit the activity of certain enzymes that break down hormones like norepinephrine, leading to increased levels of these hormones that promote fat breakdown and reduce appetite.
3. Thermogenesis: Green tea extract may enhance thermogenesis—the process by which your body generates heat by burning calories. This can lead to increased energy expenditure and potentially reduce appetite as the body adjusts to higher energy demands.
4. Impact on Dopamine Levels: Some studies suggest that green tea may affect dopamine levels in the brain, which could influence hunger signals and cravings.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Appetite Suppression
Several studies have explored the effects of green tea extract on appetite and weight management:
- A study involving obese individuals found that those consuming green tea extract lost more weight than those who did not, with reported reductions in appetite and food intake over time.
- Another study highlighted that participants taking EGCG experienced increased fat oxidation and reduced hunger levels compared to a placebo group.
- Research also indicates that regular consumption of green tea can lead to modest reductions in body weight and waist circumference, suggesting a beneficial role in long-term weight management strategies.
Additional Research Findings
Recent studies have further illuminated the relationship between green tea extract and appetite suppression:
- A meta-analysis showed that individuals consuming green tea preparations experienced an average weight loss of 2.9 pounds over 12 weeks when adhering to their regular diet. This suggests a modest but significant impact on weight management[8].
- In animal studies, mice fed a high-fat diet showed substantial reductions in body weight when supplemented with decaffeinated green tea extract combined with exercise. This combination resulted in a 27.1% reduction in body mass and significant improvements in metabolic markers[1].
- A randomized trial involving women with central obesity demonstrated significant weight loss and reductions in waist circumference after 12 weeks of high-dose EGCG treatment. Notably, levels of ghrelin—an appetite-stimulating hormone—decreased, while adiponectin—linked to fat regulation—increased[2].
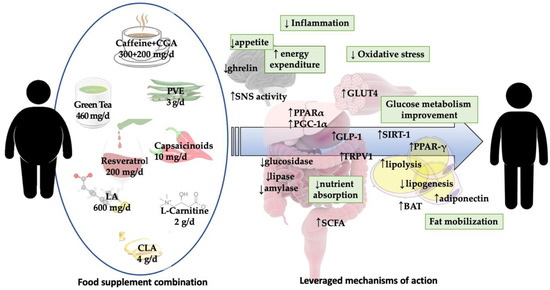
Practical Implications for Weight Management
For individuals looking to manage their weight through appetite suppression, incorporating green tea extract into their diet may offer several advantages:
- Natural Alternative: Unlike many commercial appetite suppressants, green tea extract is a natural product with additional health benefits beyond weight loss.
- Versatile Consumption: Green tea can be consumed in various forms—hot or iced tea, capsules, or as an ingredient in smoothies or health drinks—making it easy to integrate into daily routines.
- Complementary Approach: While green tea extract may help suppress appetite, it should be part of a broader strategy that includes balanced nutrition and regular physical activity for effective weight management.
Delicious Ways to Incorporate Green Tea
To maximize the benefits of green tea extract while enjoying its taste, consider these recipes:
1. Green Tea Latte: Combine brewed green tea with almond milk, honey, ground ginger, and cinnamon for a warming beverage.
```markdown
Ingredients:
- 1 bag of green tea
- 1 cup boiling water
- 1/2 cup almond milk
- 2 teaspoons honey
- 1/4 teaspoon ground ginger
- 1/4 teaspoon ground cinnamon
Instructions:
- Brew the tea bag in boiling water for 5 minutes.
- Blend with other ingredients until creamy.
```
2. Raspberry Green Tea Smoothie: Blend brewed green tea with frozen bananas and raspberries for a refreshing smoothie.
```markdown
Ingredients:
- 1 Twinings Pure Green Tea Bag
- 100ml Freshly Boiled Water
- 1 Frozen Banana
- 80g Frozen Raspberries
- 180ml Almond Milk
- 1 tsp Honey (optional)
Instructions:
- Infuse the tea bag in boiling water for 2-3 minutes.
- Blend all ingredients until smooth.
```
Conclusion
In summary, green tea extract appears to have potential as an appetite suppressant due to its unique combination of caffeine, catechins, and polyphenols. While individual results may vary, incorporating green tea into a healthy lifestyle could provide benefits for those looking to manage their weight effectively. However, it is essential to approach any weight loss strategy holistically, considering dietary habits and physical activity alongside supplement use.
FAQ
1. How much green tea should I drink for appetite suppression?
Most studies suggest consuming 2-3 cups of brewed green tea daily or taking standardized extracts equivalent to 300-500 mg of EGCG for optimal effects.
2. Are there any side effects associated with green tea extract?
While generally safe for most people, excessive consumption can lead to side effects such as insomnia, stomach upset, or headaches due to caffeine content.
3. Can I rely solely on green tea extract for weight loss?
No. While it may aid in appetite suppression and fat burning, effective weight loss requires a comprehensive approach involving diet and exercise.
4. Is there a difference between drinking green tea and taking extracts?
Yes, extracts are more concentrated in catechins and caffeine than brewed tea. Therefore, they may provide stronger effects but should be consumed with caution regarding dosage.
5. Can anyone take green tea extract?
Most people can safely consume green tea extract; however, individuals with certain medical conditions or those taking specific medications should consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Citations:
[1] https://www.psu.edu/news/research/story/research-suggests-green-tea-exercise-boost-weight-loss-health
[2] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26093535/
[3] https://www.nature.com/articles/ejcn2014143
[4] https://www.simplyquinoa.com/green-tea-latte/
[5] https://twinings.co.uk/blogs/recipes/raspberry-green-tea-smoothie
[6] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/green-tea-and-weight-loss
[7] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8406948/
[8] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280597379_Green_Tea_and_Weight_Loss_An_update_Meta-Analysis
[9] https://www.cochrane.org/CD008650/ENDOC_green-tea-for-weight-loss-and-weight-maintenance-in-overweight-or-obese-adults






























