| DeCaf-EAFree Catechins available at Botaniex: |
|
| Product Name | Brand Name | Specifications |
| Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract | DeCaf-EAFree Catechins 90 | Catechins 90%/EGCg>60/Caffeine<0.5% (Polyphenols>98%) |
| Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract | DeCaf-EAFree Catechins 80 | Catechins 80%/EGCg>55/Caffeine<0.5% (Polyphenols>95%) |
| Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract | DeCaf-EAFree Catechins 70 | Catechins 70%/EGCg>45/Caffeine<0.5% (Polyphenols>90%) |
| Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract | DeCaf-EAFree Catechins 60 | Catechins 60%/EGCg>35/Caffeine<1.0% (Polyphenols>80%) |
| ** Customized specification available upon request. |
Features and Benefits of DeCaf-EAFree Catechins (Green Tea Extracts)
· Organic:
Tea leaves selected from the Organic Certified GAP (Good Agriculture Practices) farms
Extracted and decaffeinated only with pure water, unlike the traditional process with the solvents – Ethyl Acetate
· Low content of solvent residuals: Less than 10ppm
· Low content of organic residuals: Less than 1ppm
· Low content of pesticide residuals: Less than 1ppm
· High concentration of EGCg: 35% – 65%
· Low content of caffeine: No more than 1%
· Low content of heavy metals: Less than 10ppm
· No unpleasant odor of solvent – Ethyl Acetate
Green Tea Extracts Catechins / EGCg
The tea plant is a large shrub with evergreen leaves, used medicinally for more than 5000 years in China where it originated. Tea is now the second-most consumed beverage in the world. Based on the different processes in tea making, it is categorized as Green Tea, Black Tea, Oolong Tea, White Tea, Yellow Tea and Dark Tea. A number of beneficial health effects are attributed to regular consumption of green tea and dried/powdered extracts of green tea are available as dietary supplements.
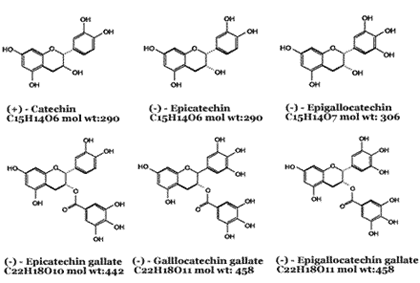
Green tea extracts is prepared by picking, lightly steaming and allowing the leaves to dry. The active constituents in green tea are a family of polyphenols (catechins) and flavonols, which possess potent antioxidant activity. Tannins, large polyphenol molecules, form the bulk of the active compounds in green tea, comprised nearly 90%of catechins. Several catechins are present in significant quantities; epicatechin (EC), epigallocatechin (EGC), epicatechin gallate (ECG) and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCg). EGCg makes up about 10-50% of the total catechins content and appears to be the most powerful of the catechins – with antioxidant activity about 25-100 times more potent than vitamins C and E. A cup of green tea may provide 10-40mg of polyphenols and has antioxidant activity greater than a serving of broccoli, spinach, carrots or strawberries. A number of commercial green tea extracts are standardized to total polyphenol content and/or EGCg content.
Latin Name | Camellia sinensis L. |  
|
Common Name | Tea |
Plant Family | Theaceae |
Part of Plant Used | Leaf |
Molecular Structure of Active Substance
Benefits
· Anti-atherogenic / Reduces cholesterol & triglycerides
· Anti-oxidant/Free radicals scavenging
· Reduces blood clotting
· Enhances immune function
· Enhances weight management
· Anti-cancer/Anti-Radiation
· Reduces platelet aggregation
· Protects against digestive and respiratory infections
· Blocks the attachment of the bacteria to the teeth associated with dental cavities
Mechanism
Because the active compounds, the catechins, found in green tea are known to possess potent antioxidant activity, they may provide beneficial health effects by protecting the body from the damaging effects of oxidative damage from free radicals. A number of chronic disease states have been associated with free radical induced oxidative damage, including cancer, heart disease, and suppressed immune function and accelerated aging.
Safety
Adverse or toxic effects of isolated tea catechins or polyphenols have not been reported in humans. Gastrointestinal disturbances and central nervous system (CNS) stimulation associated with high doses of green tea extract have been attributed to their caffeine content. Green tea extracts consumption of as much as 20 cups per day has not been associated with any significant side effects. In high doses, teas that contain caffeine may lead to restlessness, insomnia and tachycardia. Decaffeinated versions of green tea and green tea extracts are available – but due to differences in caffeine extraction methods, the amounts of phenolic/catechin compounds can vary between extracts.
It is recommended that consumers select an extract that is decaffeinated as well as standardized for total polyphenol content and/or catechin concentrations.
Applications
· Can be delivered in supplement form of a singular substance or incorporated into healthy formulas
· Easily incorporated into health beverage due to its high solubility in water
· Can be used as food additives

Dosage
· Typical dosage recommendations are for 125-500mg/day – preferably of an extract standardized to at least 60% polyphenols and/or EGCG as a marker compound (this should be equivalent to 4-10 cups of brewed green tea).
· Consult physicians if higher dosage is required.
Hot tags: Green Tea Catechins EGCg, green tea extract catechins 60%, green tea extract catechins 70%, decaffeinated catechins, green tea 90% catechins, decaffeinated green tea extract, decaf-eafree catechins, epigallocatechin gallate, egcg, green tea egcg, wholesale, China, Bulk, custom, manufacturers, manufacturing company, suppliers, factory, for sale




























