Content Menu
● Understanding Green Tea Extract
● Health Benefits of Green Tea Extract
● Caffeine Content in Green Tea Extract
● Caffeine-Free Green Tea Extract: Is It Possible?
● Benefits of Caffeine-Free Green Tea Extract
● Potential Drawbacks of Caffeine-Free Green Tea Extract
● Choosing the Right Green Tea Extract
● Safety Considerations
● Conclusion
● Questions and Answers
Green tea has been cherished for centuries, not just as a refreshing beverage but also for its numerous health benefits. In recent years, green tea extract has gained popularity as a concentrated form of these benefits, often found in supplements and various products. However, a common question arises: Can something have green tea extract and have no caffeine? This article delves into the world of green tea extract, exploring its composition, benefits, and the possibility of caffeine-free options.
Understanding Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract is a concentrated form of the compounds found in green tea leaves. It's made by steeping green tea leaves in an alcohol solution, which is then evaporated to leave behind a potent extract. This extract contains a variety of beneficial compounds, including polyphenols, catechins, and, typically, caffeine.
The main components of green tea extract include:
1. Catechins: These are powerful antioxidants, with epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) being the most abundant and well-studied.
2. Polyphenols: These compounds contribute to the antioxidant properties of green tea.
3. L-theanine: An amino acid that can promote relaxation and improve cognitive function.
4. Caffeine: A natural stimulant found in tea leaves.
5. Vitamins and minerals: Including vitamin C, B vitamins, and trace minerals.
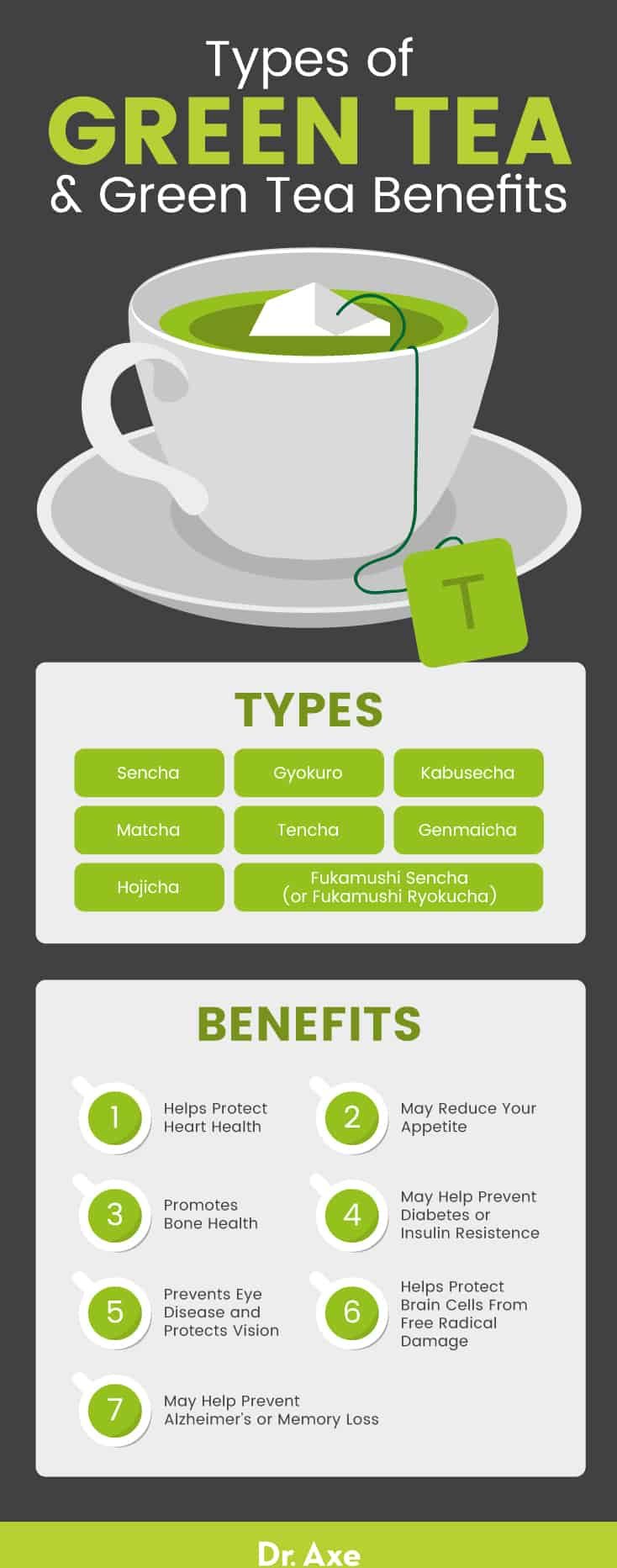
Health Benefits of Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract has been associated with numerous health benefits, which have been the subject of extensive scientific research. Some of the potential benefits include:
1. Antioxidant Properties: The high concentration of catechins, especially EGCG, provides powerful antioxidant effects. These compounds help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, potentially reducing the risk of various chronic diseases.
2. Weight Management: Some studies suggest that green tea extract may boost metabolism and increase fat burning, potentially aiding in weight loss efforts when combined with a healthy diet and exercise.
3. Heart Health: Regular consumption of green tea extract has been linked to improved cardiovascular health. It may help lower bad cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
4. Brain Function: The combination of caffeine and L-theanine in green tea extract may improve cognitive function, including memory, attention, and reaction time.
5. Cancer Prevention: While more research is needed, some studies indicate that the antioxidants in green tea extract may have cancer-fighting properties.
6. Liver Protection: Green tea extract may help protect the liver from oxidative stress and reduce the risk of liver diseases.
7. Skin Health: The antioxidants in green tea extract may help protect the skin from UV damage and signs of aging when applied topically or consumed orally.

Caffeine Content in Green Tea Extract
Typically, green tea extract contains caffeine, as it's a natural component of tea leaves. The amount of caffeine can vary depending on factors such as the type of tea leaves used, the extraction process, and the concentration of the extract. On average, a standard dose of green tea extract (usually around 200-500 mg) may contain anywhere from 14 to 40 mg of caffeine.
For comparison, an 8-ounce cup of brewed green tea contains about 25-35 mg of caffeine, while a cup of coffee can contain 95-200 mg. While the caffeine content in green tea extract is generally lower than coffee, it's still significant for those sensitive to caffeine or looking to avoid it entirely.
Caffeine-Free Green Tea Extract: Is It Possible?
The good news for those seeking the benefits of green tea extract without caffeine is that it is indeed possible to have caffeine-free options. There are two main ways to achieve this:
1. Decaffeination Process: Similar to how decaf coffee is made, green tea leaves can undergo a decaffeination process before extraction. This process removes most of the caffeine while retaining many of the beneficial compounds. Common methods include:
◆ CO2 decaffeination: Using pressurized carbon dioxide to remove caffeine.
◆ Water processing: Soaking the leaves in hot water to extract caffeine, then using the same water to reinfuse the leaves with flavors and nutrients.
◆ Ethyl acetate decaffeination: Using a chemical solvent to remove caffeine.
2. Herbal Tea Extracts: Some products labeled as "green tea extract" may actually be derived from caffeine-free herbal teas that have similar properties to green tea. For example, rooibos tea, which is naturally caffeine-free, is sometimes marketed as a green tea alternative due to its antioxidant content.

Benefits of Caffeine-Free Green Tea Extract
Opting for a caffeine-free green tea extract can offer several advantages:
1. Reduced Side Effects: Eliminating caffeine can help avoid potential side effects such as jitters, anxiety, or sleep disturbances.
2. Suitable for Sensitive Individuals: Those who are sensitive to caffeine or need to avoid it for medical reasons can still enjoy the benefits of green tea extract.
3. Evening Consumption: Caffeine-free options can be taken later in the day without risking sleep quality.
4. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant or nursing women who are advised to limit caffeine intake can consider caffeine-free alternatives.
5. Combination with Other Supplements: Caffeine-free extracts can be more easily combined with other supplements without worrying about excessive caffeine intake.
Potential Drawbacks of Caffeine-Free Green Tea Extract
While caffeine-free green tea extract offers many benefits, there are a few considerations to keep in mind:
1. Reduced Stimulant Effects: The absence of caffeine means you won't experience the energy boost and increased alertness associated with caffeinated versions.
2. Altered Composition: The decaffeination process may slightly alter the overall composition of the extract, potentially affecting some of its properties.
3. Cost: Caffeine-free versions may be more expensive due to the additional processing required.
4. Availability: Caffeine-free green tea extract may be less readily available compared to regular versions.

Choosing the Right Green Tea Extract
When selecting a green tea extract, whether caffeinated or caffeine-free, consider the following factors:
1. Standardization: Look for products standardized for EGCG content, ensuring a consistent dose of this beneficial compound.
2. Third-Party Testing: Choose products that have been tested by independent laboratories for purity and potency.
3. Caffeine Content: Check the label for caffeine content, especially if you're seeking a caffeine-free option.
4. Additional Ingredients: Some products may contain other herbs or supplements, so be aware of all ingredients.
5. Form: Green tea extract is available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and liquid extracts. Choose the form that best fits your lifestyle and preferences.
Safety Considerations
While green tea extract is generally considered safe for most people, it's important to be aware of potential risks and interactions:
1. Liver Concerns: In rare cases, high doses of green tea extract have been associated with liver problems. It's crucial to follow recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare provider if you have any liver conditions.
2. Iron Absorption: Green tea can interfere with iron absorption. If you have iron deficiency or are at risk, consider taking green tea extract between meals.
3. Medication Interactions: Green tea extract may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners and some antibiotics. Always consult with a healthcare provider before adding any new supplement to your regimen.
4. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: While caffeine-free versions may be safer, it's best to consult with a healthcare provider before using green tea extract during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
5. Caffeine Sensitivity: Even decaffeinated versions may contain trace amounts of caffeine, which could affect highly sensitive individuals.

Conclusion
Green tea extract offers a concentrated form of the beneficial compounds found in green tea, and it is indeed possible to find caffeine-free options. Whether through decaffeination processes or the use of herbal alternatives, these caffeine-free extracts provide an opportunity for individuals to enjoy the potential health benefits of green tea without the stimulant effects of caffeine.
As with any supplement, it's essential to choose high-quality products and consult with a healthcare provider, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications. By making informed choices, you can potentially harness the power of green tea extract in a way that best suits your individual needs and preferences.
Questions and Answers
Q: How much caffeine is typically in green tea extract?
A: The caffeine content in green tea extract can vary, but a standard dose (200-500 mg) typically contains 14-40 mg of caffeine.
Q: Are there any side effects of taking caffeine-free green tea extract?
A: While generally safe, some people may experience mild side effects such as stomach upset or headaches. In rare cases, high doses may affect liver function.
Q: Can caffeine-free green tea extract still help with weight loss?
A: Yes, many of the compounds responsible for potential weight loss benefits, such as EGCG, are still present in caffeine-free versions.
Q: How is caffeine removed from green tea extract?
A: Common methods include CO2 decaffeination, water processing, and ethyl acetate decaffeination.
Q: Is caffeine-free green tea extract as effective as regular green tea extract?
A: While the absence of caffeine may reduce some stimulant effects, many of the health benefits associated with green tea extract are due to other compounds that remain present in caffeine-free versions.
































