Content Menu
● Understanding Green Tea Extract
>> Caffeine Content in Green Tea Extract
● Health Benefits of Green Tea Extract
>> Antioxidant Effects
>> Weight Loss Support
>> Heart Health Benefits
● Implications for Consumers
● Potential Side Effects
● Choosing the Right Green Tea Extract
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. Does all green tea extract contain caffeine?
>> 2. How much caffeine is typically found in green tea extract?
>> 3. What are the health benefits of green tea extract?
>> 4. Can I take green tea extract if I'm sensitive to caffeine?
>> 5. Is it safe to consume high doses of green tea extract?
● Citations:
Green tea extract has gained immense popularity due to its numerous health benefits, including its rich antioxidant content and potential weight loss properties. However, a common question arises: Does all green tea extract contain caffeine? This article will explore the caffeine content in green tea extract, variations among different products, and the implications for consumers.
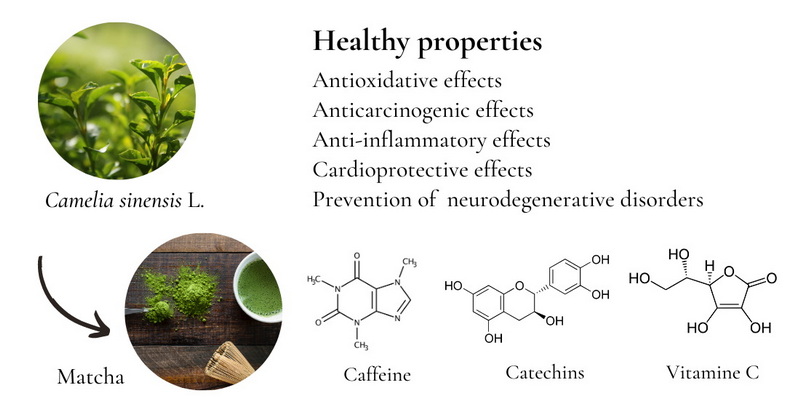
Understanding Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract is derived from the leaves of the *Camellia sinensis* plant, the same plant used to produce green tea. The extraction process concentrates its beneficial compounds, particularly catechins, which are powerful antioxidants. Among these catechins, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is the most prevalent and studied for its health benefits.
Caffeine Content in Green Tea Extract
The caffeine content in green tea extract can vary significantly based on several factors:
- Type of Product: Different brands and formulations of green tea extract can contain varying amounts of caffeine.
- Processing Method: The method used to process the leaves can affect caffeine levels. For instance, decaffeinated extracts are available that contain little to no caffeine.
- Serving Size: The amount of green tea extract per serving also influences caffeine content. Some products may offer concentrated doses that increase caffeine levels.
According to various sources, the caffeine content in green tea extract can range from as low as 2 mg to over 200 mg per serving. For example:
- NOW Foods Green Tea Extract: Approximately 32 mg of caffeine per 400 mg of extract.
- Nature's Truth Caffeine Plus Green Tea Extract: Contains around 200 mg of caffeine per serving.
- Zenwise Labs Advanced Green Tea: Offers a decaffeinated option with 0 mg of caffeine.
This variability means that not all green tea extracts will provide the same stimulant effects as traditional brewed green tea, which typically contains about 30-50 mg of caffeine per cup.
Health Benefits of Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract is praised for its health benefits, which include:
- Antioxidant Properties: Rich in catechins that combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Weight Management: Some studies suggest that it may aid in weight loss by boosting metabolism and fat oxidation.
- Heart Health: Regular consumption may reduce cholesterol levels and improve cardiovascular health.
- Cognitive Function: The combination of caffeine and L-theanine found in green tea can enhance brain function and alertness.
Antioxidant Effects
Green tea extract is particularly high in antioxidants, which play a crucial role in protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals. The primary antioxidant in green tea is EGCG, which has been shown to have various health benefits:
- Protecting brain cells from oxidative stress.
- Reducing inflammation throughout the body.
- Lowering the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer[1][20].
Weight Loss Support
Research indicates that green tea extract can assist with weight management. The catechins and caffeine work together to enhance thermogenesis—the process by which your body generates heat and energy from digesting food. This can lead to increased calorie burning. Studies have shown that participants taking green tea extract experienced greater fat oxidation during exercise compared to those who did not take it[1][4].
Heart Health Benefits
Regular consumption of green tea extract has been associated with improved heart health. It may help lower LDL cholesterol levels and triglycerides while increasing HDL cholesterol levels. Additionally, some studies suggest that it can improve blood vessel function, reducing the risk of heart disease[16][19].
Implications for Consumers
Understanding the caffeine content in green tea extract is crucial for consumers, especially those sensitive to stimulants or those who monitor their caffeine intake for health reasons. Here are some considerations:
- Read Labels Carefully: Always check the product label for specific information on caffeine content. Look for terms like "decaffeinated" if you want to avoid caffeine altogether.
- Moderation is Key: While moderate consumption is generally safe for most adults, excessive intake can lead to side effects such as insomnia, jitters, or increased heart rate.
- Consult Healthcare Providers: If you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications that may interact with caffeine, it's advisable to consult a healthcare professional before adding green tea extract to your regimen.
Potential Side Effects
While many people consume green tea extract without issues, some may experience side effects due to its caffeine content or other compounds present in the extract:
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Some users report nausea, diarrhea, or upset stomach when consuming high doses or taking it on an empty stomach[3][6].
- Liver Concerns: There have been rare reports linking high doses of green tea extract with liver damage. Individuals with pre-existing liver conditions should exercise caution and consult a doctor before use[12][18].
- Caffeine Sensitivity: Those sensitive to caffeine may experience symptoms such as anxiety, restlessness, or insomnia even at lower doses[4][13].
Choosing the Right Green Tea Extract
When selecting a green tea extract supplement, consider the following factors:
- Quality: Look for products that have been third-party tested for purity and potency. This ensures you are getting what is advertised on the label.
- Formulation: Choose between capsules, powders, or liquid extracts based on your preference. Capsules are convenient but powders can be mixed into smoothies or beverages for versatility[11][14].
- Caffeine Content: If you're sensitive to caffeine or prefer to avoid it altogether, opt for decaffeinated versions or those with lower caffeine content[13][16].
Conclusion
In summary, not all green tea extracts contain caffeine; it varies widely depending on the brand, formulation, and processing method. For those looking to enjoy the benefits of green tea without the jitters associated with high caffeine intake, decaffeinated options are available. Always consider your personal tolerance and health goals when choosing a green tea extract product.
FAQ
1. Does all green tea extract contain caffeine?
Not all green tea extracts contain caffeine; it varies by brand and formulation. Some products are specifically labeled as decaffeinated.
2. How much caffeine is typically found in green tea extract?
Caffeine levels can range from 2 mg to over 200 mg per serving depending on the product.
3. What are the health benefits of green tea extract?
Green tea extract offers various health benefits including antioxidant properties, weight management support, heart health improvement, and enhanced cognitive function.
4. Can I take green tea extract if I'm sensitive to caffeine?
If you are sensitive to caffeine, you should opt for decaffeinated versions or consult with a healthcare provider before use.
5. Is it safe to consume high doses of green tea extract?
While moderate consumption is generally safe, high doses can lead to side effects such as liver damage or gastrointestinal issues. Always follow recommended dosages on product labels.
Citations:
[1] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-benefits-of-green-tea-extract
[2] https://tigogreen.de/en/greentea-greentea-extract/
[3] https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-960/green-tea
[4] https://www.livestrong.com/article/186702-how-much-caffeine-is-in-green-tea-extract/
[5] https://www.innerbody.com/best-green-tea-extract
[6] https://www.vumc.org/poison-control/toxicology-question-week/march-12-2021-what-are-adverse-effects-green-tea-extract
[7] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/269538
[8] https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=19&contentid=greenteaextract
[9] https://medsafe.govt.nz/profs/PUArticles/Complementary%20Medicine%20Corner%20-%20Safety%20of%20Green%20Tea%20extracts.htm
[10] https://hammernutrition.com/blogs/endurance-news-weekly/green-tea-extract-in-fully-charged
[11] https://askthescientists.com/green-tea-extract/
[12] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7009618/
[13] https://www.elo.health/articles/green-tea-extract-supplements/
[14] https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/herb/green-tea
[15] https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-76714/green-tea-leaf-extract-oral/details
[16] https://health.clevelandclinic.org/green-tea-extract-a-better-way-to-boost-energy-or-not
[17] https://www.teacurry.com/blogs/tea-basics-tips/what-are-the-different-types-of-green-tea
[18] https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/green-tea
[19] https://johnshopkinshealthcare.staywellsolutionsonline.com/19,GreenTeaExtract
[20] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7084675/






























