Content Menu
● Understanding Green Tea and Its Components
>> Key Components of Green Tea:
● How Green Tea Extract Affects Appetite
● Scientific Evidence Supporting Appetite Suppression
● The Connection Between Green Tea and Hunger Hormones
● Integrating Green Tea Extract into Your Diet
● Potential Side Effects and Considerations
● The Role of Exercise in Enhancing Green Tea's Effects
● Expanding on the Benefits of Green Tea Extract
>> Metabolism Boosting Effect
>> Enhanced Fat Burning
>> Appetite Suppression Through Neurotransmitter Modulation
● Incorporating Green Tea into Your Weight Loss Journey
>> Optimal Green Tea Consumption
>> Timing Matters
● Long-term Benefits Beyond Weight Loss
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. How much green tea should I drink daily for weight loss?
>> 2. Can I drink green tea on an empty stomach?
>> 3. Does drinking green tea before meals help with weight loss?
>> 4. Are there any risks associated with taking green tea extract?
>> 5. Can I replace my morning coffee with green tea?
● Citations:
Green tea has long been celebrated for its numerous health benefits, including its potential to aid in weight management. Among its many properties, the question arises: Does green tea extract curb appetite? This article delves into the science behind green tea extract, its effects on appetite, and how it can be integrated into a healthy lifestyle.

Understanding Green Tea and Its Components
Green tea is derived from the leaves of the *Camellia sinensis* plant and is known for its rich content of antioxidants, particularly catechins. The most notable catechin is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which has been extensively studied for its health benefits, including weight loss and appetite suppression.
Key Components of Green Tea:
- Catechins: Powerful antioxidants that may boost metabolism and fat oxidation.
- Caffeine: A mild stimulant that can enhance energy expenditure and potentially reduce hunger.
- Polyphenols: Compounds that may influence various metabolic processes in the body.
How Green Tea Extract Affects Appetite
Research indicates that green tea extract may have a modest effect on appetite regulation. The mechanisms through which it operates include:
- Hormonal Influence: Green tea can affect hormones related to hunger, such as ghrelin (the hunger hormone) and leptin (the satiety hormone). Some studies suggest that EGCG may help lower ghrelin levels, thereby reducing hunger signals.
- Increased Satiety: Drinking green tea may enhance feelings of fullness after meals. A study found that participants who consumed green tea before a meal reported increased satiety compared to those who did not.
- Thermogenesis: Green tea extract may increase thermogenesis, the process by which the body generates heat and energy from digesting food. This can lead to increased calorie burning, which might indirectly influence appetite by promoting a more efficient metabolism.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Appetite Suppression
Several studies have explored the effects of green tea extract on appetite and weight loss:
1. Short-term Studies: In short-term studies, participants consuming green tea extract reported reduced hunger levels and increased feelings of fullness.
2. Long-term Studies: A comprehensive review indicated that while green tea extract can contribute to weight loss, its effects on appetite suppression are less pronounced. The overall weight loss attributed to green tea was modest compared to lifestyle changes like diet and exercise.
3. Mixed Results: Some research has shown no significant impact on appetite regulation when comparing green tea extract with placebo groups. This suggests that individual responses to green tea may vary widely.
The Connection Between Green Tea and Hunger Hormones
Recent research has suggested a potential link between green tea consumption and the secretion of GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1), a hormone produced in the gut that signals satiety. GLP-1 slows gastric emptying and influences brain regions responsible for hunger regulation. While some researchers theorize that green tea might stimulate GLP-1 production, current evidence remains inconclusive. For instance, a clinical trial involving individuals with Type 2 diabetes found no significant difference in GLP-1 production between those taking green tea extract and those receiving a placebo[1].
Integrating Green Tea Extract into Your Diet
To harness the potential benefits of green tea extract for appetite control and weight management, consider the following tips:
- Daily Consumption: Aim for 2-3 cups of brewed green tea daily or consider supplements with standardized EGCG content. This amount is generally considered safe and effective for most individuals.
- Combine with Healthy Habits: For optimal results, incorporate green tea into a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains while maintaining regular physical activity.
- Stay Hydrated: Sometimes feelings of hunger are mistaken for thirst. Drinking water or herbal teas alongside green tea can help manage appetite effectively.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
While green tea is generally safe for most people, excessive consumption—especially in supplement form—can lead to side effects such as:
- Caffeine Sensitivity: Some individuals may experience anxiety or insomnia due to caffeine content in green tea extracts.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: High doses of green tea extract can cause stomach upset or nausea in some users.
- Drug Interactions: Green tea extracts may interact with certain medications. It's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
The Role of Exercise in Enhancing Green Tea's Effects
Incorporating exercise into your routine while consuming green tea may amplify its benefits for weight loss. Studies have shown that combining physical activity with green tea consumption can enhance fat oxidation during exercise[2]. This suggests that individuals looking to maximize their weight loss efforts should consider integrating both strategies into their lifestyle.
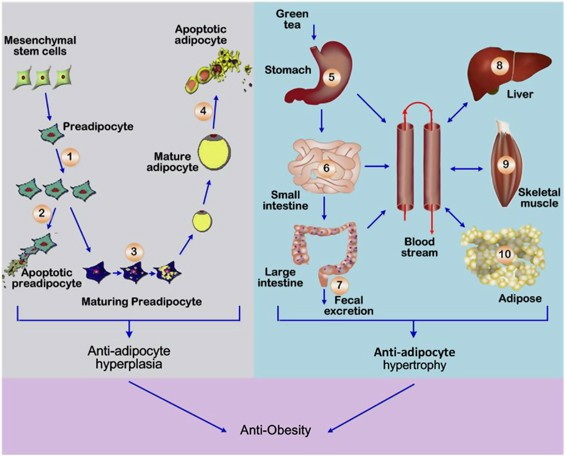
Expanding on the Benefits of Green Tea Extract
To further understand how green tea extract aids in weight management beyond just curbing appetite, we must explore its metabolic effects more deeply.
Metabolism Boosting Effect
One of the key ways green tea helps in weight loss is through boosting metabolism. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition published research showing that green tea extract can increase the body's metabolic rate, leading to greater calorie burn and fat oxidation[3]. This is attributed largely to the thermogenic properties of catechins, which enhance energy expenditure and fat oxidation during both rest and exercise.
Enhanced Fat Burning
Green tea has been found to enhance the body's ability to burn fat, particularly during exercise. A study published in the American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism reported that green tea extract increases the rate at which the body burns fat during moderate-intensity exercise[4]. This suggests that when combined with regular physical activity, consuming green tea can accelerate the process of weight loss.
Appetite Suppression Through Neurotransmitter Modulation
Green tea may also contribute to weight loss by reducing appetite through its influence on neurotransmitters in the brain[5]. Compounds within green tea can modulate levels of certain neurotransmitters associated with hunger signals, helping individuals feel less inclined to eat excessively throughout the day.
Incorporating Green Tea into Your Weight Loss Journey
Incorporating green tea into a weight loss regimen can be a beneficial process. To maximize its effects:
Optimal Green Tea Consumption
- Dosage: To effectively harness the weight loss benefits of green tea, it is recommended to consume about 2-3 cups per day.
- Brewing Methods: Proper brewing can enhance effectiveness; steeping time should be between 2-3 minutes in hot water (not boiling) preserves beneficial compounds[6].
Timing Matters
Drinking green tea about 30 minutes before meals can maximize its metabolism-boosting effects[7]. Avoid consuming it late at night due to caffeine content affecting sleep patterns.
Long-term Benefits Beyond Weight Loss
Beyond aiding in weight management, regular consumption of green tea has been linked to several long-term health benefits:
- Heart Health: Drinking at least three cups daily has been associated with reduced risk factors for heart disease[8].
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Studies indicate that catechins may improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels over time[9].
- Cancer Prevention: Some research suggests that antioxidants in green tea could lower risks associated with various types of cancer due to their protective effects on cells[10].
Conclusion
In summary, while green tea extract shows promise in curbing appetite through various mechanisms such as hormonal regulation and increased satiety, its effects are modest when compared to other lifestyle changes like diet and exercise. Individuals looking to manage their weight should consider incorporating green tea as part of a holistic approach that includes healthy eating habits and regular physical activity.
In conclusion, while drinking or supplementing with green tea extract may offer some benefits regarding appetite control and metabolism enhancement, it should not be viewed as a standalone solution for significant weight loss. Instead, it should be integrated into an overall healthy lifestyle comprising balanced nutrition and regular physical activity for optimal results.

FAQ
1. How much green tea should I drink daily for weight loss?
Aim for 2-3 cups of brewed green tea daily or consider supplements with standardized EGCG content for effective results.
2. Can I drink green tea on an empty stomach?
While many people do consume it this way, some may experience stomach upset. It's best to see how your body reacts.
3. Does drinking green tea before meals help with weight loss?
Yes, drinking green tea before meals may enhance feelings of fullness and reduce overall calorie intake.
4. Are there any risks associated with taking green tea extract?
Yes, excessive consumption can lead to side effects such as anxiety due to caffeine or gastrointestinal issues.
5. Can I replace my morning coffee with green tea?
Yes! Green tea contains caffeine but in lower amounts than coffee, making it a good alternative if you're looking to reduce caffeine intake.
Citations:
[1] https://www.nytimes.com/2024/09/24/well/green-tea-weight-loss-ozempic.html
[2] https://nessey.newmedialab.cuny.edu/files/research/en-green-tea-helps-in-weight-loss-g3st_53ggft0hv
[3] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26093535/
[4] https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/nutrition/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022.1084455/full
[5] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38031409/
[6] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-benefits-of-green-tea-extract
[7] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8406948/
[8] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39350601/
[9] https://www.hollandandbarrett.com/the-health-hub/weight-management/weight-loss/can-you-drink-green-tea-for-weight-loss/
[10] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320540
[11] https://hsph.harvard.edu/news/green-tea-healthy-habit/
[12] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-natural-appetite-suppressants
[13] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2161831322010973
[14] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320540
[15] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S026156141500134X
[16] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0002916522042022
[17] https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/15502783.2024.2411029?src=exp-la
[18] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/269538
[19] https://new-beauty.com/sg-en/blog/slimming-treatments/green-tea-weight-loss-review/
[20] https://health.clevelandclinic.org/green-tea-extract-a-better-way-to-boost-energy-or-not
[21] https://www.nytimes.com/2024/09/24/well/green-tea-weight-loss-ozempic.html
[22] https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-960/green-tea
[23] https://www.health.com/nutrition/benefits-green-tea
[24] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4025876/
[25] https://www.healthline.com/health/benefits-of-green-tea-for-skin
[26] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6412948/
[27] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2855614/






























