Content Menu
● The Science Behind Green Tea Extract
>> Key Components of Green Tea
>> Mechanisms of Action
● Does Green Tea Extract Actually Reduce Appetite?
● Green Tea and Appetite Hormones
● Practical Implications of Green Tea Consumption
● Additional Benefits of Green Tea Extract
● How to Incorporate Green Tea into Your Diet
● Potential Side Effects of Green Tea Extract
● Historical Context of Green Tea
● Cultural Significance
● Modern Research on Green Tea Extract
● Practical Tips for Maximizing Benefits
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. How much green tea should I drink daily for weight loss?
>> 2. Can I rely solely on green tea for weight loss?
>> 3. Are there any side effects of consuming green tea extract?
>> 4. How does green tea affect metabolism?
>> 5. Is there a difference between drinking green tea and taking supplements?
● Citations:
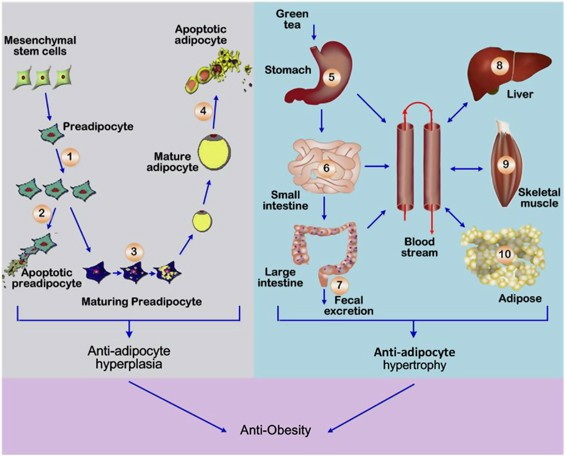
Green tea has long been celebrated for its health benefits, particularly in weight management and appetite suppression. This article delves into the science behind green tea extract, exploring its potential to reduce appetite, enhance metabolism, and contribute to weight loss.
The Science Behind Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract is derived from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant and is rich in bioactive compounds, particularly catechins and caffeine. The most notable catechin is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which has been extensively studied for its health benefits.
Key Components of Green Tea
- Catechins: These are powerful antioxidants that may help in fat oxidation and energy expenditure.
- Caffeine: A stimulant that can boost metabolism and enhance fat burning.
Mechanisms of Action
1. Increased Metabolism: Research indicates that green tea extract can boost metabolic rates by 3-4% over 24 hours, leading to increased calorie burning even at rest.
2. Fat Oxidation: Studies have shown that green tea can enhance fat oxidation during exercise, making it a popular choice among fitness enthusiasts.
3. Appetite Regulation: Some studies suggest that green tea may influence hormones related to appetite regulation, such as ghrelin and leptin. However, results are mixed, with some studies showing no significant impact on appetite suppression.
Does Green Tea Extract Actually Reduce Appetite?
While there is some evidence suggesting that green tea extract may help reduce appetite, the results are not universally conclusive.
- Positive Findings: Some studies report that participants consuming green tea or EGCG experienced reduced hunger levels and increased feelings of fullness. For instance, a study indicated that individuals taking EGCG reported greater satiation after meals compared to those on a placebo.
- Contradictory Evidence: Conversely, other research has found no significant differences in hunger or caloric intake between those consuming green tea extract and those who did not. A systematic review concluded that while there might be some appetite-suppressing effects for certain individuals, the overall impact is minimal.
Green Tea and Appetite Hormones
The relationship between green tea and appetite-regulating hormones is complex:
- Ghrelin: Often referred to as the "hunger hormone," ghrelin levels typically increase before meals and decrease after eating. Some studies suggest that green tea may help modulate ghrelin levels, potentially leading to reduced hunger.
- Leptin: This hormone signals satiety to the brain. Some research indicates that green tea may help improve leptin sensitivity, which could assist in regulating appetite.
Practical Implications of Green Tea Consumption
To harness the potential benefits of green tea for weight management:
- Daily Intake: Consuming 2-3 cups of green tea daily is generally recommended for optimal benefits without excessive caffeine intake.
- Combination with Other Strategies: For effective weight loss, it's crucial to combine green tea consumption with a balanced diet and regular exercise. Green tea should not be viewed as a standalone solution but rather as a complementary tool in a broader weight management strategy.
Additional Benefits of Green Tea Extract
In addition to its potential effects on appetite and metabolism, green tea extract offers several other health benefits:
- Antioxidant Properties: The high concentration of antioxidants in green tea helps combat oxidative stress in the body, which can contribute to various chronic diseases.
- Heart Health: Regular consumption of green tea has been linked to improved cardiovascular health by reducing LDL cholesterol levels and improving blood vessel function.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Some studies suggest that green tea may help regulate blood sugar levels, making it beneficial for individuals with insulin sensitivity or type 2 diabetes.
- Mental Clarity: The combination of caffeine and L-theanine found in green tea can enhance brain function, improving mood, reaction time, and memory.
How to Incorporate Green Tea into Your Diet
Incorporating green tea into your daily routine can be simple and enjoyable:
- Brewed Tea: The most common way to consume green tea is by brewing loose leaves or bags in hot water. Aim for water temperatures around 160°F to 180°F (70°C to 80°C) to avoid bitterness.
- Smoothies: Adding matcha powder (a concentrated form of green tea) to smoothies can provide a nutrient boost while enhancing flavor.
- Cooking: Use brewed green tea or matcha in cooking; it can be added to soups, sauces, or even baked goods for an extra layer of flavor and nutrition.
- Supplements: If you find it challenging to consume enough green tea through beverages alone, consider supplements containing standardized extracts. However, consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Potential Side Effects of Green Tea Extract
While moderate consumption of green tea is generally safe for most people, excessive intake can lead to side effects:
- Caffeine Sensitivity: Individuals sensitive to caffeine may experience anxiety, insomnia, or digestive issues when consuming large amounts of green tea extract.
- Liver Health Concerns: There have been rare reports linking high doses of concentrated green tea extract supplements with liver damage. It's essential to stick with recommended dosages and consult a healthcare provider if you have pre-existing liver conditions.
Historical Context of Green Tea
Green tea has been consumed for thousands of years. Originating from China over 4,000 years ago, it was initially used for medicinal purposes before gaining popularity as a beverage. Historical texts reference its use in traditional Chinese medicine as an aid for digestion and overall health enhancement.
As trade routes expanded across Asia into Europe during the Middle Ages, the appreciation for this beverage spread globally. Today, countries like Japan and China still honor traditional methods of brewing and serving this ancient drink through ceremonies like the Japanese Tea Ceremony (Chanoyu).
Cultural Significance
Green tea holds significant cultural importance in various societies:
- Japan: In Japan, matcha (powdered green tea) plays a crucial role in cultural rituals and ceremonies. It symbolizes harmony and respect among participants during traditional gatherings.
- China: In Chinese culture, drinking loose-leaf teas signifies hospitality; offering guests high-quality teas reflects respect and honor toward them.
Modern Research on Green Tea Extract
Recent studies continue exploring the multifaceted benefits of green tea extract beyond appetite suppression:
1. Weight Management Studies: A meta-analysis published in Obesity Reviews found that participants using catechin-rich supplements lost more weight than those who did not use any supplements over periods ranging from 12 weeks up to six months.
2. Cardiovascular Health Research: Research published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition highlighted how regular consumption could lower blood pressure levels significantly among hypertensive patients over time.
3. Cancer Prevention Studies: Some epidemiological studies suggest an association between regular consumption of green tea and reduced risks for certain types of cancers such as breast cancer or prostate cancer due largely due its antioxidant properties inhibiting tumor growth at cellular levels.
Practical Tips for Maximizing Benefits
To maximize the health benefits associated with drinking or supplementing with green tea extract:
- Choose high-quality sources—look for organic options free from additives.
- Experiment with different types—try various blends like jasmine or mint-infused varieties if you find plain flavors unappealing.
- Monitor your body's response—pay attention to how your body reacts after consuming different amounts; adjust accordingly based on personal tolerance levels regarding caffeine intake!
Conclusion
In summary, while green tea extract may have some potential to reduce appetite and aid in weight loss through various mechanisms such as increased metabolism and fat oxidation, the evidence remains mixed regarding its effectiveness as an appetite suppressant. Individual responses can vary significantly; thus, it may be beneficial for some while less effective for others.
For those looking to incorporate green tea into their diet for potential weight management benefits, it is advisable to do so alongside healthy eating habits and physical activity. The integration of this ancient beverage into modern dietary practices offers numerous health benefits beyond just appetite reduction.
In conclusion once again—while evidence suggests potential appetite-reducing effects linked directly back towards regular consumption patterns involving both brewed teas & concentrated extracts alike—it's essential not only focus solely upon these aspects but also consider overall lifestyle choices when aiming towards achieving long-term success related towards maintaining healthy body weights effectively!
By understanding both historical context along with modern-day applications surrounding this ancient beverage—individuals can make informed decisions about incorporating it into their daily lives!

FAQ
1. How much green tea should I drink daily for weight loss?
Drinking 2-3 cups of green tea daily is generally recommended for weight loss benefits without excessive caffeine intake.
2. Can I rely solely on green tea for weight loss?
No, while green tea may assist in weight management, it should be combined with a balanced diet and regular exercise for effective results.
3. Are there any side effects of consuming green tea extract?
In moderate amounts, green tea is considered safe; however, excessive consumption can lead to side effects such as nausea or insomnia due to caffeine content.
4. How does green tea affect metabolism?
Green tea has been shown to increase metabolic rate by enhancing fat oxidation and energy expenditure.
5. Is there a difference between drinking green tea and taking supplements?
Yes, supplements often contain higher concentrations of catechins compared to brewed green tea; however, both forms can provide health benefits.
Citations:
[1] https://www.nytimes.com/2024/09/24/well/green-tea-weight-loss-ozempic.html
[2] https://nessey.newmedialab.cuny.edu/files/research/en-green-tea-helps-in-weight-loss-g3st_53ggft0hv
[3] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/green-tea-and-weight-loss
[4] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-natural-appetite-suppressants
[5] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320540
[6] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P_-n9yU9tVw
[7] https://www.casi.org/node/1257
[8] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-benefits-of-green-tea-extract
[9] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8406948/
[10] https://japanesetea.sg/japanese-tea-pedia/health-benefits-of-green-tea/
[11] https://www.uchicagomedicine.org/forefront/news/2000/february/green-tea-derivative-causes-loss-of-appetite-weight-loss-in-rats
[12] https://www.hollandandbarrett.com/the-health-hub/weight-management/weight-loss/can-you-drink-green-tea-for-weight-loss/
[13] https://wa.kaiserpermanente.org/kbase/topic.jhtml?docId=hn-3916005
[14] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26093535/
[15] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320540
[16] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8406948/
[17] https://health.clevelandclinic.org/green-tea-extract-a-better-way-to-boost-energy-or-not
[18] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-natural-appetite-suppressants
[19] https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/9/2238
[20] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VxdGaxpUW0Q
[21] https://www.noon.com/green-tea-extract-weight-loss-pills-to-reduce-belly-fat-green-coffee-bean-extract-appetite-suppressant-fat-burner-for-women-and-men-vegan-glutenfree-fat-burner-supplement-60-capsules/Z9B2454300F20FBB42989Z/p
[22] https://www.netmeds.com/health-library/post/weight-loss-5-must-to-try-energising-teas-to-burn-fat-infographic
[23] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dWZq7WcZQbc
[24] https://www.pinterest.com/pin/528469337505765591/
[25] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W1Bj7sKWxi8
[26] https://www.istockphoto.com/illustrations/green-tea-weight-loss
[27] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IGtyQTlsFGw
[28] https://www.pinterest.com/pin/507851295480045086/
[29] https://www.youtube.com/hashtag/greenteaweightloss
[30] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SG3d13bxPsk
[31] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=khq7vo4x_BQ






























