Content Menu
● Introduction
● Understanding Green Tea Extract Composition
● Scientific Research on Optimal Dosage
● Health Benefits and Mechanisms of Action
● Safety Considerations and Recommended Dosage Guidelines
● Potential Side Effects and Precautions
● Optimizing Absorption and Effectiveness
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
Green tea extract has emerged as one of the most studied natural supplements in modern scientific research, garnering significant attention for its diverse health benefits and therapeutic potential. This concentrated form of green tea contains powerful compounds, particularly catechins and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which are responsible for its numerous health-promoting properties. Understanding the optimal dosage of green tea extract is crucial for maximizing its benefits while ensuring safety and effectiveness. This comprehensive analysis explores the scientific evidence behind green tea extract supplementation, recommended dosages, and important considerations for daily consumption.

Understanding Green Tea Extract Composition
The potency and effectiveness of green tea extract largely depend on its composition, particularly its concentration of bioactive compounds. Green tea extract is primarily composed of polyphenols, with EGCG being the most abundant and therapeutically significant component. Modern extraction methods concentrate these beneficial compounds, making green tea extract significantly more potent than traditional brewed green tea. The standardization of these extracts typically ensures that each serving contains a specific amount of polyphenols and EGCG, allowing for more precise dosing and consistent results.
Scientific Research on Optimal Dosage
Extensive research has been conducted to determine the optimal dosage of green tea extract for various health benefits. Studies have shown that the effective dose can vary depending on the intended health outcome and individual factors. Clinical trials have demonstrated that the safe and effective daily intake of EGCG, the primary active compound in green tea extract, should not exceed 338 mg when taken as a solid supplement. This recommendation is based on comprehensive safety assessments and considers both the benefits and potential risks of supplementation.
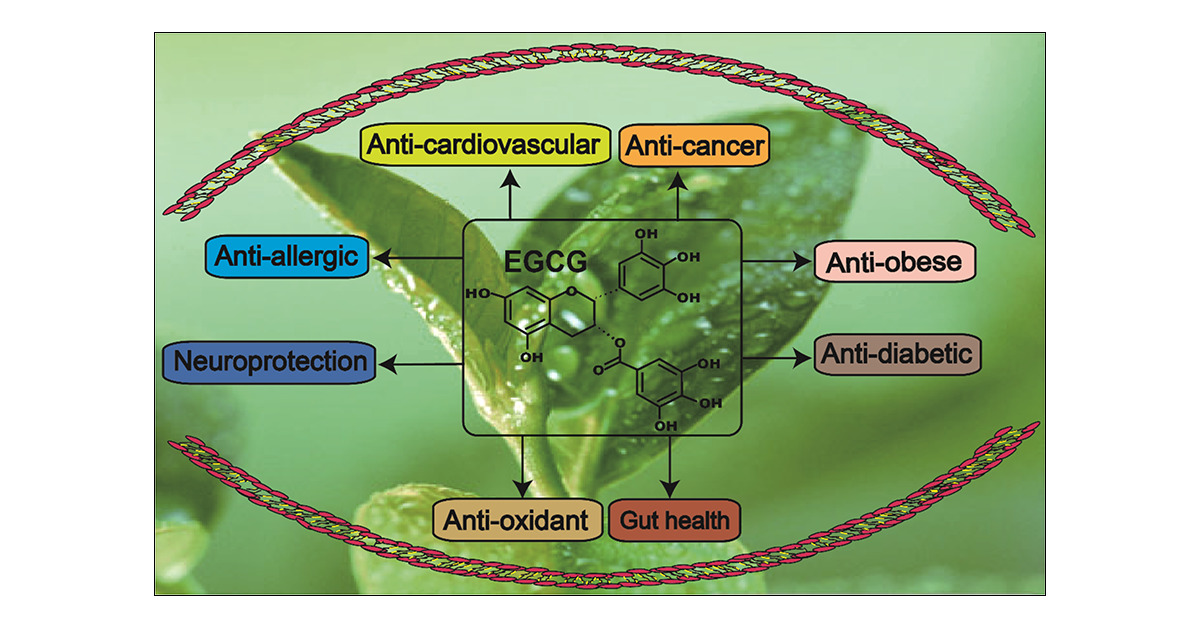
Health Benefits and Mechanisms of Action
Green tea extract works through multiple mechanisms to promote health and prevent disease. Its primary modes of action include:
1. Antioxidant Protection: The polyphenols in green tea extract neutralize harmful free radicals and reduce oxidative stress throughout the body.
2. Metabolic Enhancement: The compounds in green tea extract can boost metabolism and support healthy weight management.
3. Cardiovascular Support: Regular supplementation may help maintain healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
4. Cognitive Function: The bioactive compounds support brain health and may help protect against age-related cognitive decline.
Safety Considerations and Recommended Dosage Guidelines
When determining the appropriate dosage of green tea extract, several factors must be considered to ensure safe and effective supplementation. The recommended daily intake varies based on the form of supplementation and individual factors:
1. For standardized supplements: The general recommendation is to start with a lower dose and gradually increase it while monitoring tolerance.
2. Timing considerations: It's often advised to take green tea extract between meals to optimize absorption and minimize potential side effects.
3. Individual factors: Age, health status, and concurrent medications can all influence the appropriate dosage.

Potential Side Effects and Precautions
While green tea extract is generally considered safe, awareness of potential side effects and necessary precautions is essential. Some individuals may experience:
1. Digestive issues when taken on an empty stomach
2. Sleep disturbances if taken late in the day
3. Possible interactions with certain medications
4. Rare cases of liver sensitivity in susceptible individuals
Optimizing Absorption and Effectiveness
To maximize the benefits of green tea extract supplementation, several factors can enhance its absorption and effectiveness:
1. Taking the supplement with a small amount of healthy fat
2. Maintaining consistent daily dosing schedules
3. Staying well-hydrated throughout the day
4. Combining supplementation with a healthy lifestyle
Conclusion
The optimal daily dosage of green tea extract depends on various factors, including individual health goals, tolerance, and the specific formulation being used. Based on current scientific evidence, a daily intake of 300-400 mg of EGCG from green tea extract appears to be both safe and effective for most healthy adults. However, it's crucial to start with a lower dose and gradually increase it while monitoring individual response and consulting with healthcare providers when necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the best time to take green tea extract?
A: The optimal time is typically in the morning or early afternoon, between meals, to maximize absorption and prevent sleep disturbances.
Q: Can I take green tea extract on an empty stomach?
A: It's generally recommended to take green tea extract with or shortly after meals to minimize the risk of digestive discomfort.
Q: How long does it take to see benefits from green tea extract supplementation?
A: Results can vary, but most studies show initial benefits within 8-12 weeks of consistent supplementation.
Q: Are there any groups who should avoid green tea extract?
A: Pregnant women, individuals with liver conditions, and those sensitive to caffeine should consult healthcare providers before supplementation.
Q: Can I take green tea extract with other supplements?
A: While generally safe, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider about potential interactions with other supplements or medications.































