Content Menu
● Introduction
● The Science Behind Green Tea Extract
● Safe Dosage Guidelines
● Potential Benefits and Risks
● Factors Affecting Tolerance
● Signs of Excessive Consumption
● Best Practices for Supplementation
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
Green tea extract has gained significant popularity as a dietary supplement due to its potential health benefits and concentrated form of beneficial compounds. This concentrated form of green tea's active ingredients has become increasingly prevalent in the supplement market, available in various forms including capsules, powders, and liquid extracts. Understanding the appropriate dosage and potential risks of green tea extract consumption is crucial for safe supplementation and optimal health benefits.
The Science Behind Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract is a concentrated form of the compounds found in green tea leaves, particularly catechins and their derivatives. The primary active compound in green tea extract is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which is responsible for many of its potential health benefits. The extraction process concentrates these beneficial compounds, making them more potent than traditional brewed green tea.
Safe Dosage Guidelines
The determination of safe green tea extract dosage involves careful consideration of multiple factors, including individual tolerance, overall health status, and the concentration of active compounds. Research has shown that the body can generally tolerate varying amounts of green tea extract, but there are important thresholds to consider for safe consumption. The concentration of EGCG is particularly important when determining appropriate dosage levels, as this compound can have both beneficial and potentially harmful effects depending on the amount consumed.
Potential Benefits and Risks
Green tea extract offers numerous potential health benefits when consumed within safe limits. These benefits include antioxidant properties, potential metabolism enhancement, and possible cardiovascular health support. However, excessive consumption can lead to adverse effects. The liver is particularly sensitive to high doses of green tea extract, and careful attention must be paid to dosage to avoid potential hepatotoxicity.

Factors Affecting Tolerance
Individual tolerance to green tea extract can vary significantly based on several factors. These include body weight, existing health conditions, medication interactions, and timing of consumption. The method of consumption, whether with or without food, can also impact how the body processes green tea extract. Understanding these factors is crucial for determining appropriate individual dosage levels.
Signs of Excessive Consumption
Recognizing the signs of excessive green tea extract consumption is essential for maintaining safe supplementation practices. Common indicators of overconsumption may include digestive discomfort, sleep disturbances, and in some cases, liver-related symptoms. Being aware of these signs allows for proper adjustment of dosage and prevention of potential adverse effects.
Best Practices for Supplementation
To ensure safe consumption of green tea extract, following certain best practices is recommended. These include starting with lower doses and gradually increasing as tolerance is established, taking supplements with food rather than on an empty stomach, and maintaining proper hydration. Regular monitoring of how the body responds to supplementation is also crucial for safe long-term use.
Conclusion
The safe consumption of green tea extract requires careful attention to dosage and individual response. While this supplement offers numerous potential benefits, the key to safe supplementation lies in understanding appropriate dosage levels and recognizing personal tolerance limits. Consulting with healthcare providers before beginning supplementation is always recommended, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those taking medications.
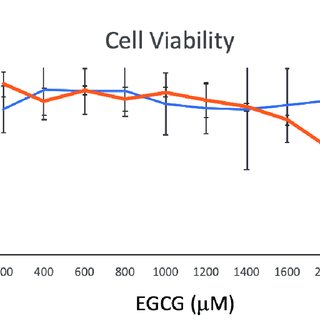
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the recommended daily dose of green tea extract?
A: The generally recommended daily dose ranges from 250-500 mg of standardized green tea extract, containing no more than 338 mg of EGCG.
Q: Can green tea extract interact with medications?
A: Yes, green tea extract can interact with various medications, including blood thinners and certain antidepressants. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting supplementation.
Q: Should green tea extract be taken with food?
A: Yes, it's generally recommended to take green tea extract with food to minimize potential gastrointestinal discomfort and optimize absorption.
Q: How can I recognize if I'm taking too much green tea extract?
A: Signs of excessive intake may include nausea, stomach pain, headaches, sleep problems, irritability, or irregular heartbeat.
Q: Is green tea extract safe for everyone?
A: While generally safe for most adults, certain individuals should exercise caution, including pregnant women, those with liver conditions, and people sensitive to caffeine.































