Content Menu
● Understanding Heartburn
>> Symptoms of Heartburn
● The Role of Green Tea Extract
>> Mechanisms Leading to Heartburn
● Who is at Risk?
● Scientific Perspectives on Green Tea and Heartburn
● Recommendations for Consumption
● Additional Health Benefits of Green Tea
● Potential Side Effects Beyond Heartburn
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. Can drinking green tea cause heartburn?
>> 2. How much green tea is safe to drink daily?
>> 3. Should I drink green tea on an empty stomach?
>> 4. Are there alternatives to traditional green tea if I have GERD?
>> 5. What should I do if I experience heartburn after drinking green tea?
● Citations:
Green tea, derived from the leaves of the *Camellia sinensis* plant, has gained immense popularity due to its numerous health benefits. It is rich in antioxidants, particularly catechins, which are believed to provide various health advantages, including weight loss, improved brain function, and reduced risk of certain diseases. However, despite its benefits, many individuals report experiencing heartburn after consuming green tea or its extracts. This article explores the connection between green tea extract and heartburn, examining the underlying causes, symptoms, and potential solutions.

Understanding Heartburn
Heartburn is a common condition characterized by a burning sensation in the chest or throat. It occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, leading to discomfort. This reflux can be triggered by various factors, including diet, lifestyle choices, and specific medical conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Symptoms of Heartburn
- Burning sensation in the chest
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
- Difficulty swallowing
- Sensation of a lump in the throat
- Chronic cough or hoarseness
The Role of Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract is a concentrated form of green tea that contains high levels of catechins and caffeine. While it is often marketed for its health benefits, excessive consumption can lead to side effects, including heartburn.
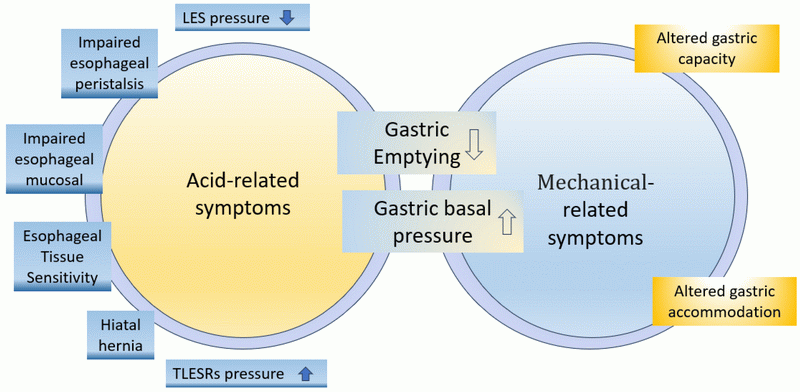
Mechanisms Leading to Heartburn
1. Caffeine Content: Green tea contains caffeine, which may relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). This relaxation can allow stomach acid to escape into the esophagus, causing heartburn.
2. Tannins: Green tea is rich in tannins, which can increase stomach acidity. Higher acidity levels can irritate the esophagus and lead to heartburn symptoms.
3. Stomach Irritation: For some individuals, green tea can irritate the stomach lining, particularly when consumed on an empty stomach. This irritation may exacerbate heartburn symptoms.
4. Excessive Consumption: Drinking large amounts of green tea or taking high doses of green tea extract can overwhelm the digestive system and lead to increased acid production.
Who is at Risk?
Certain individuals may be more susceptible to experiencing heartburn after consuming green tea extract:
- Those with GERD: Individuals diagnosed with GERD should be cautious with green tea as it may exacerbate their symptoms.
- Sensitive Individuals: People who are sensitive to caffeine or tannins may experience heartburn even with moderate consumption.
- Pregnant Women: Due to hormonal changes affecting digestion during pregnancy, women may find that they are more prone to heartburn when consuming caffeinated beverages like green tea.
Scientific Perspectives on Green Tea and Heartburn
Research on the relationship between green tea consumption and heartburn has produced mixed results. Some studies suggest that while green tea has beneficial properties, it might also contribute to GERD symptoms in certain populations. A meta-analysis indicated that while some observational studies found no significant association between tea drinking and GERD risk, others suggested a positive correlation[1].
Theophylline, a component found in tea, may contribute to relaxing the LES, leading to esophageal acid reflux[1]. However, other studies have shown that moderate consumption of green tea does not significantly increase GERD risk[10]. This inconsistency highlights the need for further research into how individual responses to green tea may vary based on genetic predispositions and existing health conditions.
Recommendations for Consumption
To minimize the risk of heartburn while enjoying green tea extract:
- Moderation is Key: Limit intake to 2-3 cups per day and avoid high-dose supplements unless prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Avoid on an Empty Stomach: Consume green tea after meals rather than on an empty stomach to reduce irritation.
- Choose Decaffeinated Options: If caffeine sensitivity is a concern, consider decaffeinated green tea options.
- Monitor Symptoms: Keep track of your body's response to green tea and adjust your consumption accordingly.
Additional Health Benefits of Green Tea
Despite potential side effects like heartburn, green tea remains one of the healthiest beverages available. Its numerous health benefits include:
- Antioxidant Properties: The high levels of catechins in green tea help combat oxidative stress and reduce inflammation in the body.
- Weight Management: Studies have shown that green tea can aid in weight loss by boosting metabolism and increasing fat oxidation[7].
- Cardiovascular Health: Regular consumption of green tea has been linked to lower cholesterol levels and improved heart health[6].
- Cancer Prevention: Some research suggests that the antioxidants in green tea may help reduce the risk of certain types of cancer[7].
Potential Side Effects Beyond Heartburn
In addition to heartburn, excessive consumption of green tea can lead to other side effects:
- Gastrointestinal Issues: High doses may cause nausea, diarrhea, or abdominal pain due to increased acidity or caffeine content[8].
- Nervousness and Insomnia: The caffeine present in green tea can lead to anxiety or sleep disturbances if consumed excessively[6].
- Liver Damage: Rare cases of liver problems have been reported with high doses of green tea extract supplements[5].
Conclusion
While green tea extract offers numerous health benefits, it can also cause heartburn in some individuals due to its caffeine and tannin content. Understanding your body's reactions and adjusting your consumption habits can help mitigate these effects. If you frequently experience heartburn after consuming green tea or its extracts, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
FAQ
1. Can drinking green tea cause heartburn?
Yes, drinking green tea can cause heartburn due to its caffeine content and tannins that increase stomach acidity.
2. How much green tea is safe to drink daily?
Moderation is key; limiting intake to 2-3 cups per day is generally considered safe for most people.
3. Should I drink green tea on an empty stomach?
It is advisable not to drink green tea on an empty stomach as it may irritate the stomach lining and exacerbate heartburn symptoms.
4. Are there alternatives to traditional green tea if I have GERD?
Yes, consider decaffeinated green tea or herbal teas that do not contain caffeine or tannins.
5. What should I do if I experience heartburn after drinking green tea?
If you experience heartburn after drinking green tea, reduce your intake and consult with a healthcare professional if symptoms persist.
Citations:
[1] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6358326/
[2] https://www.practo.com/healthfeed/green-tea-side-effects-and-who-must-avoid-it-3626/post
[3] https://senchateabar.com/blogs/blog/green-tea-side-effects
[4] https://www.rxlist.com/supplements/green_tea.htm
[5] https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=19&contentid=GreenTeaExtract
[6] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/269538
[7] https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/herb/green-tea
[8] https://www.vumc.org/poison-control/toxicology-question-week/march-12-2021-what-are-adverse-effects-green-tea-extract
[9] https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-960/green-tea
[10] https://www.livestrong.com/article/488168-is-green-tea-bad-for-acid-reflux/






























