Content Menu
● Understanding Degenerative Disc Disease
● The Role of Green Tea Extract
>> Mechanisms of Action
● Supporting Research
● Practical Implications
● Lifestyle Modifications
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is Degenerative Disc Disease?
>> 2. How does Green Tea Extract help with DDD?
>> 3. Are there any side effects of taking Green Tea Extract?
>> 4. How much Green Tea Extract should I take for potential benefits?
>> 5. Can lifestyle changes enhance the effectiveness of Green Tea Extract for DDD?
● Citations:
Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD) is a prevalent condition that affects the spine, particularly as individuals age. It can lead to chronic pain, reduced mobility, and a significant decrease in quality of life. As researchers explore various treatment options, one natural remedy gaining attention is green tea extract, specifically its active compound, Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG). This article delves into the potential of green tea extract in treating DDD, examining its mechanisms of action, supporting research, and practical implications.

Understanding Degenerative Disc Disease
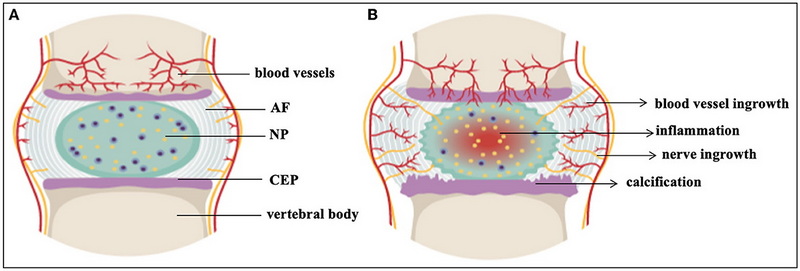
Degenerative Disc Disease refers to the gradual deterioration of the intervertebral discs in the spine. These discs serve as cushions between the vertebrae, allowing for flexibility and movement. Over time, factors such as aging, injury, or repetitive stress can lead to disc degeneration. Symptoms often include:
- Chronic back pain
- Numbness or tingling in the limbs
- Weakness in the legs
- Reduced range of motion
While traditional treatments for DDD include physical therapy, pain medications, and surgical interventions, they often do not address the underlying biological processes causing the degeneration.
The Role of Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract is derived from the leaves of *Camellia sinensis* and is rich in polyphenols, particularly EGCG. This compound has been extensively studied for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Research suggests that EGCG may have a protective effect on intervertebral discs by targeting several key mechanisms involved in disc degeneration.
Mechanisms of Action
1. Anti-inflammatory Effects: EGCG has been shown to inhibit inflammatory pathways that contribute to disc degeneration. By reducing inflammation, it may alleviate pain and slow down the progression of DDD.
2. Antioxidant Properties: Oxidative stress plays a significant role in cellular aging and degeneration. EGCG acts as a potent antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative damage to disc cells.
3. Cellular Protection: Studies indicate that EGCG can protect intervertebral disc cells from apoptosis (programmed cell death) induced by oxidative stress. This protective effect may help maintain disc integrity and function.
4. Extracellular Matrix Preservation: The extracellular matrix (ECM) is crucial for disc health. Research suggests that EGCG can help preserve ECM components, thus supporting disc structure and function.
5. Circadian Rhythm Regulation: Recent studies have indicated that EGCG may influence circadian rhythms in intervertebral disc cells. Disruption of these rhythms can exacerbate degenerative processes; thus, restoring them could provide an additional therapeutic benefit[9].
Supporting Research
Several studies have explored the efficacy of green tea extract in relation to degenerative disc disease:
- Preclinical Studies: Research has demonstrated that EGCG can reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in intervertebral disc cells. In one study, EGCG treatment led to decreased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and improved cell viability under oxidative stress conditions[1].
- Animal Models: In vivo studies using animal models have shown promising results where EGCG administration resulted in reduced pain behaviors and improved histological outcomes in degenerated discs[2].
- Mechanistic Insights: Further investigations have revealed that EGCG activates specific signaling pathways associated with cellular survival and ECM maintenance, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic agent for DDD[4].
- Clinical Implications: A systematic review highlighted that green tea consumption correlates with improved joint health due to its anti-inflammatory effects[5]. This insight could be extrapolated to DDD management as well.

Practical Implications
While the research surrounding green tea extract is promising, it is essential to consider practical implications for individuals suffering from DDD:
- Supplementation: Green tea extract supplements are widely available and can be incorporated into daily routines. However, it is crucial to consult with healthcare providers before starting any new supplement regimen.
- Dietary Inclusion: Drinking green tea regularly may offer additional health benefits beyond DDD management. Incorporating green tea into a balanced diet can enhance overall well-being due to its antioxidant properties.
- Holistic Approach: While green tea extract shows potential in treating DDD, it should be considered part of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes physical therapy, exercise, and lifestyle modifications.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to supplementing with green tea extract or drinking green tea regularly, certain lifestyle changes can further support spinal health:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact exercises such as swimming or walking can strengthen back muscles and improve flexibility without putting excessive strain on the spine.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on the spine and intervertebral discs. Green tea may assist with weight management through its metabolism-boosting properties[3].
- Posture Awareness: Practicing good posture while sitting or standing can alleviate undue stress on the spine. Ergonomic furniture may also help maintain proper alignment during daily activities.
Conclusion
Green tea extract, particularly its active component EGCG, presents a promising avenue for treating degenerative disc disease due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. While preliminary research supports its efficacy in reducing inflammation and protecting intervertebral discs from degeneration, further clinical studies are necessary to establish definitive treatment protocols.
As always, individuals should consult healthcare professionals before making significant changes to their treatment plans or incorporating new supplements into their diets.
FAQ
1. What is Degenerative Disc Disease?
Degenerative Disc Disease is a condition characterized by the deterioration of intervertebral discs in the spine, leading to pain and reduced mobility.
2. How does Green Tea Extract help with DDD?
Green Tea Extract contains EGCG, which has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that may protect against disc degeneration.
3. Are there any side effects of taking Green Tea Extract?
While generally safe for most people when consumed in moderation, high doses may lead to gastrointestinal issues or interact with certain medications.
4. How much Green Tea Extract should I take for potential benefits?
Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations on dosage based on individual health needs.
5. Can lifestyle changes enhance the effectiveness of Green Tea Extract for DDD?
Yes! Combining green tea extract with regular exercise, physical therapy, and a healthy diet can improve overall outcomes for managing DDD.
Citations:
[1] https://orthotech.ethz.ch/research/tissue-mechanobiology/natural-compounds-for-the-treatment-of-painful-disc-degeneration.html
[2] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2694926/
[3] https://caringmedical.com/prolotherapy-news/green-tea-joint-pain/
[4] https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1155/2016/7031397
[5] https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Summary-of-studies-on-the-effects-of-green-tea-and-epigallocatechin-gallate-EGCG-on_tbl1_346452618
[6] https://scolination.com/blogs/diet-nutrition/the-health-benefits-of-green-tea-for-scoliosis
[7] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27119009/
[8] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/382106387_Exploring_the_antioxidant_realm_of_green_tea_From_extraction_to_fortification
[9] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8599576/
[10] https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-67133-z






























