Content Menu
● Understanding Green Tea and Its Components
● The Benefits of Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract
● Mechanisms Behind Energy Provision
● Comparing Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract with Regular Green Tea
● Potential Side Effects
● Research Findings Supporting Energy Provision
● Decaffeination Methods and Their Impact
● Incorporating Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract into Your Diet
● Decaf Green Tea's Role in Mental Clarity
● The Importance of Antioxidants
● Combining Exercise with Decaf Green Tea Extract
● Lifestyle Considerations
● Final Thoughts on Choosing Quality Products
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. Can decaffeinated green tea extract help with weight loss?
>> 2. Is there any caffeine in decaffeinated green tea?
>> 3. How does decaffeinated green tea compare to regular green tea?
>> 4. Can I drink decaffeinated green tea at night?
>> 5. Are there any side effects associated with decaffeinated green tea extract?
● Citations:
Decaffeinated green tea extract (dGTE) has gained popularity as a health supplement, particularly among those who wish to avoid caffeine while still reaping the benefits associated with green tea. This article explores whether decaffeinated green tea extract can provide energy and enhance overall well-being, alongside its potential benefits, mechanisms of action, and comparisons to its caffeinated counterpart.
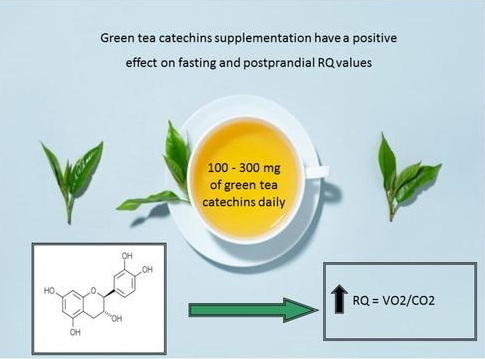
Understanding Green Tea and Its Components
Green tea, derived from the leaves of the *Camellia sinensis* plant, is celebrated for its health benefits primarily due to its rich content of polyphenols, particularly catechins. The most studied catechin is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), known for its potent antioxidant properties.
- Caffeine Content: Regular green tea contains about 20-50 mg of caffeine per 8-ounce cup, which contributes to its stimulating effects. In contrast, decaffeinated green tea typically contains only about 2-4 mg of caffeine per cup, making it a suitable option for those sensitive to caffeine or looking to reduce their intake.
- Antioxidant Properties: Both regular and decaffeinated green tea contain antioxidants that help combat oxidative stress in the body. However, the decaffeination process can affect the levels of these beneficial compounds.
The Benefits of Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract
1. Weight Management: Research indicates that decaffeinated green tea extract may aid in weight management by enhancing fat oxidation. A study showed that participants taking dGTE experienced a significant increase in fat oxidation rates compared to those on a placebo.
2. Exercise Performance: Another study found that dGTE improved exercise performance and body composition in recreationally active individuals. Participants who consumed dGTE showed better endurance and fat utilization during exercise.
3. Antioxidant Effects: Decaffeinated green tea retains a substantial amount of its antioxidants, which help protect cells from damage and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
4. Cognitive Benefits: Some studies suggest that decaffeinated green tea may improve memory function. The presence of the amino acid L-theanine in green tea can promote relaxation without drowsiness, potentially enhancing cognitive performance.
5. Cardiovascular Health: Regular consumption of green tea has been linked to lower cholesterol levels and improved heart health. These benefits are also observed with decaffeinated versions, as they still contain beneficial catechins.
Mechanisms Behind Energy Provision
While dGTE contains minimal caffeine, its energy-boosting effects are primarily attributed to its catechin content:
- Fat Oxidation: The catechins in dGTE can enhance the body's ability to oxidize fat during exercise, leading to improved energy utilization.
- Metabolic Rate: Although caffeine is known for boosting metabolic rate, studies suggest that catechins alone can also contribute to increased energy expenditure through thermogenesis and fat oxidation processes.
- Stress Reduction: The calming effects of L-theanine found in green tea may contribute to a more balanced energy level, reducing fatigue caused by stress.
Comparing Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract with Regular Green Tea
| Feature | Regular Green Tea | Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract |
| Caffeine Content | 20-50 mg per cup | 2-4 mg per cup |
| Antioxidant Levels | Higher (depends on brewing) | Slightly lower but still significant |
| Weight Loss Potential | Yes | Yes |
| Cognitive Benefits | Yes | Yes |
| Exercise Performance | Yes | Yes |
Potential Side Effects
While decaffeinated green tea extract is generally safe for most people, some may experience side effects:
- Digestive Issues: High doses of green tea extract can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Liver Health Concerns: Some studies have associated high doses of concentrated green tea extracts with liver toxicity; thus, moderation is key.

Research Findings Supporting Energy Provision
Recent studies have explored the impact of decaffeinated green tea extract on various health parameters:
- A study published in *Nutrients* examined the effects of dGTE on fat oxidation and body composition among overweight individuals engaged in regular exercise. Results indicated that participants taking dGTE experienced a significant improvement in maximal fat oxidation and substrate utilization during exercise[2][19].
- Another research effort involving mice demonstrated that those consuming dGTE while exercising exhibited substantial reductions in body weight and improvements in metabolic health markers compared to those not receiving the extract[3]. This suggests that similar outcomes could be realized by humans.
Decaffeination Methods and Their Impact
The method used for decaffeination can influence the antioxidant content of green tea extracts:
- Water Processing Method: This method retains approximately 92% of the original antioxidant power of the tea. It is considered one of the best methods for preserving beneficial compounds while removing caffeine.
- Chemical Extraction Methods: Some methods may result in only about 18% retention of antioxidants. Therefore, consumers should be aware of how their decaffeinated products are processed when seeking health benefits[9].
Incorporating Decaffeinated Green Tea Extract into Your Diet
To maximize the benefits of decaffeinated green tea extract:
- Supplementation: Consider taking high-quality supplements standardized for EGCG content. For instance, some products provide more EGCG than several cups of brewed green tea[1].
- Brewing Techniques: If you prefer drinking decaf green tea, opt for brands that use water processing methods to ensure higher antioxidant retention.
- Balanced Diet: Combine dGTE with a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins for optimal health benefits.
Decaf Green Tea's Role in Mental Clarity
Decaffeinated green tea extract not only supports physical energy but also mental clarity:
- Cognitive Function: Studies have shown that L-theanine can enhance alpha brain wave activity associated with relaxation without drowsiness[5]. This effect may lead to improved focus during tasks requiring sustained attention.
- Memory Improvement: Research indicates that regular consumption of both caffeinated and decaffeinated forms can benefit memory retention and recall abilities[11]. This is particularly relevant for older adults looking to maintain cognitive function as they age.
The Importance of Antioxidants
Antioxidants play a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals—unstable molecules that can cause cellular damage:
- Oxidative Stress Reduction: The polyphenols found in dGTE are powerful antioxidants that help mitigate oxidative stress linked to chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer[12].
- Cellular Repair: Antioxidants support cellular repair mechanisms by protecting DNA from damage caused by free radicals[20].
Combining Exercise with Decaf Green Tea Extract
Integrating physical activity with dGTE consumption enhances overall health outcomes:
- Synergistic Effects on Fat Loss: Combining regular exercise with dGTE has been shown to maximize fat loss compared to either intervention alone[3].
- Improved Recovery Times: The anti-inflammatory properties inherent in EGCG may aid recovery post-exercise by reducing muscle soreness[14].
Lifestyle Considerations
For optimal results when using decaf green tea extract:
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in both aerobic exercises (like walking or cycling) and strength training for comprehensive fitness benefits.
- Hydration: Maintain adequate hydration levels as part of your daily routine; this supports metabolic processes influenced by both exercise and nutrient intake from supplements like dGTE[20].
Final Thoughts on Choosing Quality Products
When selecting a decaffeinated green tea product or supplement:
- Check Labels Carefully: Look for products that specify their extraction methods and polyphenol content.
- Research Brands: Choose reputable brands known for quality control practices ensuring purity and potency[17].
By understanding how decaffeinated green tea extract works within your body and making informed choices regarding supplementation and lifestyle habits, you can harness its potential benefits effectively.
Conclusion
Decaffeinated green tea extract offers numerous health benefits while providing a milder energy boost compared to its caffeinated counterpart. Its ability to enhance fat oxidation and improve exercise performance makes it an excellent choice for those looking to manage weight or increase physical endurance without the jitters associated with caffeine.
Incorporating dGTE into your daily routine can support overall health while allowing you to enjoy the calming effects of this ancient beverage.

FAQ
1. Can decaffeinated green tea extract help with weight loss?
Yes, studies indicate that decaffeinated green tea extract can enhance fat oxidation and support weight management efforts.
2. Is there any caffeine in decaffeinated green tea?
Yes, decaffeinated green tea contains a small amount of caffeine—typically around 2-4 mg per cup.
3. How does decaffeinated green tea compare to regular green tea?
Decaffeinated green tea has lower caffeine content but retains many antioxidants and health benefits found in regular green tea.
4. Can I drink decaffeinated green tea at night?
Yes, due to its low caffeine content, it is suitable for consumption in the evening without affecting sleep.
5. Are there any side effects associated with decaffeinated green tea extract?
While generally safe, high doses may cause digestive issues or liver concerns; moderation is recommended.
Citations:
[1] https://www.lifeextension.com/vitamins-supplements/item00954/decaffeinated-mega-green-tea-extract
[2] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33652910/
[3] https://www.psu.edu/news/research/story/research-suggests-green-tea-exercise-boost-weight-loss-health
[4] https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=19&contentid=greenteaextract
[5] https://greatist.com/eat/decaf-green-tea-benefits
[6] https://health.clevelandclinic.org/green-tea-extract-a-better-way-to-boost-energy-or-not
[7] https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/endocrinology/articles/10.3389/fendo.2021.736724/full
[8] https://nioteas.com/blogs/green-tea/green-tea-side-effects
[9] https://matcha.com/blogs/news/decaffeinated-coffee-vs-matcha-green-tea-powder-the-benefits-of-drinking-matcha-tea-instead-of-decaf-coffee
[10] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/269538
[11] https://www.livestrong.com/article/368182-health-benefits-of-decaf-green-tea/
[12] https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/4/776
[13] https://senchateabar.com/blogs/blog/green-tea-side-effects
[14] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4307170/
[15] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/349653387_The_Impact_of_Decaffeinated_Green_Tea_Extract_on_Fat_Oxidation_Body_Composition_and_Cardio-Metabolic_Health_in_Overweight_Recreationally_Active_Individuals
[16] https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-960/green-tea
[17] https://pureprescriptions.com/product/green-tea-extract-decaffeinated-pure-encapsulations/
[18] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547925/
[19] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7996723/
[20] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-benefits-of-green-tea-extract
[21] http://www.gssiweb.org/research/article/metabolic-response-to-decaffeinated-green-tea-extract-during-rest-and-moderate-intensity-exercise
[22] https://www.oncotarget.com/article/18858/text/






























