Content Menu
● What Are Tannins?
>> Types of Tannins
● Tannin Content in Green Tea
>> Factors Affecting Tannin Levels
● Health Benefits of Tannins in Green Tea
● Potential Drawbacks of Tannins
● How to Maximize Benefits While Minimizing Risks
● Cultural Significance of Green Tea
>> Japanese Tea Ceremony
>> Chinese Tea Culture
● Scientific Research on Green Tea Extract
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What are the main types of tannins found in green tea?
>> 2. How do tannins affect the flavor of green tea?
>> 3. Is it possible to consume too much green tea due to its tannin content?
>> 4. Do all teas contain tannins?
>> 5. Can I reduce the tannin content when brewing green tea?
● Citations:
Green tea, derived from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant, is renowned for its numerous health benefits, largely attributed to its rich content of polyphenols, particularly catechins. Among these compounds, tannins play a significant role in both the flavor profile and health effects of green tea. This article delves into the presence of tannins in green tea extract, their properties, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
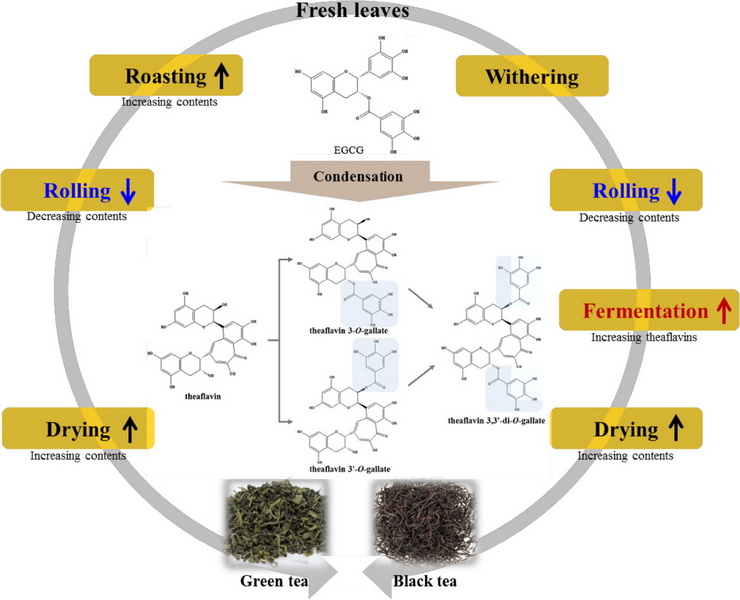
What Are Tannins?
Tannins are a class of polyphenolic compounds found in various plants, including tea, wine, and certain fruits. They are known for their astringent taste and ability to bind with proteins and other macromolecules. In plants, tannins serve as a defense mechanism against herbivores and pathogens due to their bitter taste and potential toxicity at high concentrations.
Types of Tannins
Tannins can be broadly categorized into two types:
- Hydrolyzable Tannins: These are composed of phenolic acids and can be broken down into smaller molecules upon hydrolysis.
- Condensed Tannins: Also known as proanthocyanidins, these are formed from flavonoid units and are more stable than hydrolyzable tannins.
Tannin Content in Green Tea
Research indicates that green tea contains a moderate amount of tannins compared to other types of tea. The concentration of tannins in green tea typically ranges from 2.65% to 3.11% by weight, which is significantly lower than that found in black tea (up to 15%). The primary tannin present in green tea is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a type of catechin that contributes to many of the health benefits associated with green tea.
Factors Affecting Tannin Levels
The amount of tannin extracted from green tea can be influenced by several factors:
- Type of Tea: Different varieties of green tea may have varying levels of tannins based on their cultivation and processing methods.
- Brewing Time and Temperature: Longer steeping times and higher temperatures can increase the extraction of tannins, leading to a more astringent flavor.
- Quality of Leaves: Higher quality leaves tend to have lower tannin levels compared to lower quality ones.
Health Benefits of Tannins in Green Tea
Tannins in green tea offer several health benefits due to their antioxidant properties:
- Antioxidant Activity: Tannins help neutralize free radicals in the body, reducing oxidative stress and lowering the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: The anti-inflammatory effects of tannins may help reduce inflammation-related conditions by inhibiting inflammatory markers.
- Antimicrobial Effects: Some studies suggest that tannins possess antibacterial properties that can combat various pathogens, including those responsible for gastrointestinal infections.
- Weight Management: Tannins may also play a role in weight management by influencing metabolism. Some research indicates that they can enhance fat oxidation and improve metabolic rate, potentially aiding in weight loss efforts.
- Cardiovascular Health: The consumption of tannin-rich beverages like green tea has been linked to improved cardiovascular health. Studies suggest that regular intake may lower blood pressure and improve cholesterol levels by reducing LDL (bad cholesterol) oxidation.
Potential Drawbacks of Tannins
While tannins provide numerous health benefits, excessive consumption can lead to some negative effects:
- Nutrient Absorption Inhibition: High levels of tannins may hinder the absorption of certain nutrients, particularly non-heme iron from plant sources. This could potentially lead to iron deficiency in susceptible individuals.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Some people may experience stomach irritation or nausea when consuming large amounts of tannin-rich beverages like green tea.
- Interference with Medications: Tannins can also interact with certain medications, particularly those that require specific pH levels for optimal absorption. It is advisable for individuals on medication to consult with healthcare professionals regarding their consumption of green tea.

How to Maximize Benefits While Minimizing Risks
To enjoy the benefits of green tea while minimizing potential drawbacks associated with tannin consumption, consider the following tips:
- Moderation is Key: Limit your intake to 2-3 cups per day to avoid excessive consumption while still reaping the health benefits.
- Choose Quality Over Quantity: Opt for high-quality loose-leaf green teas rather than low-grade bagged teas, as they tend to have better flavor profiles and lower tannin content.
- Mind Your Brewing Method: Use cooler water (around 160°F or 70°C) and steep for shorter periods (1-3 minutes) to reduce tannin extraction while still enjoying the flavor and health benefits.
Cultural Significance of Green Tea
Green tea holds significant cultural importance across various regions. In countries like Japan and China, it is not just a beverage but an integral part of social rituals and traditions.
Japanese Tea Ceremony
In Japan, the chanoyu or tea ceremony emphasizes aesthetics, mindfulness, and respect. It showcases the preparation and serving of matcha (powdered green tea), highlighting the cultural significance attached to this beverage.
Chinese Tea Culture
In China, green tea has been consumed for thousands of years not only for its flavor but also for its medicinal properties. Different regions produce distinct varieties such as Longjing (Dragon Well) and Biluochun (Green Snail Spring), each celebrated for unique tastes and aromas.
Scientific Research on Green Tea Extract
Numerous studies have explored the health implications associated with green tea extract:
- A study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition indicated that regular consumption could significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes due to improved insulin sensitivity.
- Another research piece in The Journal of Nutrition highlighted how catechins could enhance fat oxidation during exercise, making them beneficial for weight management strategies.
Conclusion
In summary, green tea extract does contain tannins, primarily in the form of catechins like EGCG. These compounds contribute significantly to the health benefits associated with green tea while also influencing its flavor profile. However, moderation is key; while tannins offer protective effects against various diseases, excessive intake may lead to nutrient absorption issues or gastrointestinal discomfort. By understanding both the advantages and potential drawbacks associated with tannin consumption in green tea extract, individuals can make informed choices that align with their health goals.

FAQ
1. What are the main types of tannins found in green tea?
The primary type of tannin found in green tea is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which belongs to the catechin family.
2. How do tannins affect the flavor of green tea?
Tannins contribute to the astringent taste and overall flavor profile of green tea. Higher concentrations can lead to a more pronounced bitterness.
3. Is it possible to consume too much green tea due to its tannin content?
Yes, excessive consumption can lead to side effects such as stomach irritation and hindered nutrient absorption, particularly iron.
4. Do all teas contain tannins?
Yes, all true teas derived from Camellia sinensis, including black, oolong, white, and green teas, contain varying levels of tannins.
5. Can I reduce the tannin content when brewing green tea?
Yes, you can reduce the extraction of tannins by using lower water temperatures and shorter steeping times.
Citations:
[1] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/tannins-in-tea
[2] https://ir.uitm.edu.my/id/eprint/106284/1/106284.pdf
[3] https://www.mindbodygreen.com/articles/tannins-in-tea
[4] https://tecompanytea.com/blogs/tea-atelier/what-are-tannins-in-tea
[5] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7478251/
[6] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-benefits-of-green-tea-extract
[7] https://www.teamiblends.com/blogs/lifestyle/tannins-tea-positive-negative
[8] https://bostonteawrights.com/tea-tannins-part-2-green-tea/
[9] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aUgY7luf9hU
[10] https://redblossomtea.com/blogs/red-blossom-blog/what-are-tannins-in-tea
[11] https://www.japanesegreentea.in/blogs/japanese-green-tea-lovers-in-india/green-tea-science-part-1-polyphenols-catechins-and-egcg-15-commonly-asked-questions-and-how-you-can-benefit
[12] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7478251/
[13] https://www.jocpr.com/articles/determination-of-tannin-content-by-titrimetric-method-from-different-types-of-tea.pdf
[14] https://blog.piquelife.com/tannins-in-tea/
[15] https://senchateabar.com/blogs/blog/green-tea-side-effects
[16] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6412948/
[17] https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=19&contentid=greenteaextract
[18] https://patents.google.com/patent/DE10106216A1/en
[19] https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Total-phenolic-tannin-and-flavonoid-contents-of-white-green-and-black-tea-extracts_tbl1_270482106
[20] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/269538
[21] https://www.japanesegreenteain.com/blogs/green-tea-and-health/catechins
[22] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RIbff5iD0GQ
[23] https://www.istockphoto.com/de/bot-wall?returnUrl=%2Fde%2Fphotos%2Fbenefits-of-green-tea
[24] https://tigogreen.de/en/greentea-greentea-extract/
[25] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x5nnjklqXXI
[26] https://www.health.com/nutrition/benefits-green-tea
[27] https://www.facebook.com/MiaJasperGold/videos/tannins-part-1happy-herbal-teatuesday-today-we-are-talking-about-tannins-and-how/569951087695677/
[28] https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-composition-of-the-extracts-extracted-from-fresh-leaves-and-green-tea-with-various_tbl1_280824740
[29] https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLiyo9-RPWA8y8P92ZI_d-SmJLxQ2kV1My
[30] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PkrCEKVZzjM
[31] https://www.tiktok.com/@dr.m_/video/6997213339348733190
[32] https://bostonteawrights.com/tea-tannins-part-2-green-tea/
[33] https://www.botaniex.com/does-green-tea-extract-contain-tannins.html
[34] https://teatsy.com/blogs/blog/what-are-tannins-in-tea
[35] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/tannins-in-tea
[36] https://monkschai.com/en-us/blogs/news/tannins-in-tea-what-to-know
[37] https://www.mindbodygreen.com/articles/tannins-in-tea
[38] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283364529_Total_Phenolic_Compounds_And_Tannins_Content_Of_Bancha_Green_Tea_Camellia_Sinensis_Depending_On_Extraction_Conditions






























