Content Menu
● Understanding Testosterone
● The Role of Green Tea Extract
>> Mechanisms of Action
● Scientific Evidence: Mixed Results
● Factors Influencing Outcomes
● Detailed Studies on Green Tea's Effects on Testosterone
>> Animal Studies
>> Human Studies
● Conclusion
● FAQs
>> 1. Does drinking green tea lower testosterone levels?
>> 2. How does green tea affect male fertility?
>> 3. Can I drink green tea every day?
>> 4. What is the best way to consume green tea for health benefits?
>> 5. Are there any side effects from consuming too much green tea?
● Citations:
Green tea, derived from the leaves of Camellia sinensis, has been consumed for centuries and is celebrated for its numerous health benefits. Among these purported benefits, there is ongoing debate regarding its impact on testosterone levels in men. This article explores the relationship between green tea extract and testosterone, examining scientific studies, mechanisms of action, and potential implications for health.
Understanding Testosterone
Testosterone is a key hormone in the male body, responsible for various physiological functions including:
- Development of male reproductive tissues
- Promotion of secondary sexual characteristics
- Regulation of libido and sexual function
- Maintenance of muscle mass and bone density
Maintaining optimal testosterone levels is crucial for overall health. Low testosterone can lead to a range of issues such as decreased libido, fatigue, depression, and loss of muscle mass.
The Role of Green Tea Extract
Green tea contains several bioactive compounds, notably catechins like epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which are believed to contribute to its health benefits. These compounds exhibit antioxidant properties and may influence various biological processes, including hormone regulation.
Mechanisms of Action
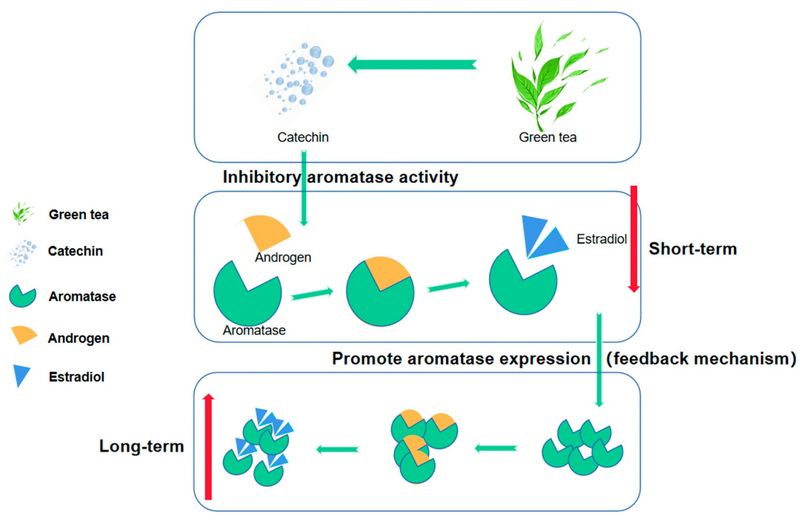
1. Inhibition of 5-alpha-reductase:
- Green tea catechins inhibit the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). By reducing DHT levels, testosterone may remain more stable in the bloodstream.
2. Anti-inflammatory Effects:
- Chronic inflammation can adversely affect testosterone production. Green tea's anti-inflammatory properties help protect Leydig cells in the testes—responsible for testosterone production—from damage.
3. Adaptogenic Properties:
- Green tea acts as an adaptogen, potentially helping to stabilize hormone levels. This means it can boost testosterone if levels are low or help regulate excessive testosterone levels.
4. Impact on Liver Function:
- The liver plays a crucial role in hormone metabolism. Green tea supports liver health, which can lead to better hormonal balance and stable testosterone levels.
Scientific Evidence: Mixed Results
Research findings on the effects of green tea on testosterone levels are mixed:
- Increased Testosterone: Some studies suggest that moderate consumption of green tea may help maintain or even increase testosterone levels by reducing inflammation and inhibiting DHT production.
- Decreased Testosterone: Conversely, other studies indicate that high doses of green tea extract can lead to a significant reduction in testosterone levels in animal models. For example, certain studies on rats have shown that administration of EGCG resulted in lower testosterone production by Leydig cells.
- No Significant Change: Additionally, some research has found no significant impact on testosterone levels with regular green tea consumption.
Factors Influencing Outcomes
The variability in study results may be attributed to several factors:
- Dosage: The amount of green tea or extract consumed plays a critical role. High doses may lead to decreased testosterone while moderate consumption may support hormonal balance.
- Duration of Consumption: Long-term versus short-term consumption can yield different effects on hormone levels.
- Individual Differences: Genetic factors and existing health conditions can influence how an individual's body responds to green tea.
Detailed Studies on Green Tea's Effects on Testosterone
Animal Studies
Several studies have examined the effects of green tea extract on testosterone levels in animal models:
1. Study on Rats:
- A study found that administering a high dose of EGCG led to a significant reduction in serum testosterone levels in male rats. This was attributed to the inhibition of steroidogenic enzymes involved in testosterone synthesis[1][6].
2. Long-term Administration:
- Another study administered aqueous green tea extract to male rats over 90 days and observed no significant changes in body weight or serum testosterone levels[1]. This suggests that moderate doses may not adversely affect hormonal balance.
3. Spermatogenesis Impact:
- Research indicated that while some doses impaired spermatogenesis by affecting sperm count and motility, others showed an increase in sperm concentration without altering testosterone levels significantly[5][6].
Human Studies
Human studies have also explored the relationship between green tea consumption and hormone levels:
1. Controlled Trials:
- A controlled trial involving daily supplementation with EGCG did not produce consistent changes in serum testosterone among participants[11]. This suggests that individual responses to green tea may vary widely.
2. Dietary Influence:
- Observational studies have linked regular green tea consumption with altered steroid profiles but did not consistently demonstrate significant changes in testosterone levels[12][14].
3. Potential Masking Effects:
- Interestingly, research has indicated that compounds found in green tea might mask elevated testosterone levels during doping tests by inhibiting the enzyme responsible for excreting testosterone from the body[4][16]. This raises questions about the implications for athletes consuming high amounts of green tea.
Conclusion
The relationship between green tea extract and testosterone is complex and not fully understood. While moderate consumption may support healthy testosterone levels through various mechanisms such as reducing inflammation and inhibiting DHT production, excessive intake could potentially lower testosterone levels due to direct inhibition of Leydig cell function.
FAQs
1. Does drinking green tea lower testosterone levels?
Research shows mixed results; moderate consumption may support healthy levels while high doses could decrease them.
2. How does green tea affect male fertility?
Some studies suggest that green tea can improve sperm parameters like concentration and vitality but may also affect hormone levels that regulate spermatogenesis.
3. Can I drink green tea every day?
Yes, moderate daily consumption is generally considered safe and beneficial for most people.
4. What is the best way to consume green tea for health benefits?
Drinking 2-3 cups of brewed green tea daily is often recommended to maximize health benefits without excessive intake.
5. Are there any side effects from consuming too much green tea?
Excessive consumption can lead to side effects such as digestive issues, increased heart rate, and potential negative impacts on hormone balance.
Citations:
[1] https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-72319-6
[2] https://academic.oup.com/endo/article-abstract/141/3/980/2988065?redirectedFrom=fulltext&login=false
[3] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3584908/
[4] https://www.newscientist.com/article/mg21328574-700-green-tea-could-mask-testosterone-doping/
[5] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7498455/
[6] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4788727/
[7] https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/05/120521115351.htm
[8] https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3168/full/v3/i4/32.htm
[9] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3735300/
[10] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26319564/
[11] https://aacrjournals.org/cancerpreventionresearch/article/5/3/393/49953/Effect-of-2-Month-Controlled-Green-Tea
[12] https://www.wada-ama.org/en/resources/scientific-research/effect-tea-consumption-steroid-profile-healthy-volunteers
[13] https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/10/121018151940.htm
[14] https://www.worldteanews.com/Features/green-tea-masks-testosterone-doping-tests
[15] https://cdnsciencepub.com/doi/10.1139/apnm-2015-0123
[16] https://www.cbsnews.com/news/green-tea-could-cloud-olympic-doping-tests/
[17] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22429924/
[18] https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/6/1439
[19] https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/british-journal-of-nutrition/article/putative-effects-of-green-tea-on-body-fat-an-evaluation-of-the-evidence-and-a-review-of-the-potential-mechanisms/2B360DD0B64C7A1CD603FE13D369026B






























