Content Menu
● Introduction to L-Theanine and Green Tea
>> L-Theanine Structure and Properties
● Impact of L-Theanine on Digestive Health
>> 1. Relaxation and Stress Reduction
>> 2. Modulation of Gut Microbiota
>> 3. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
>> 4. Influence on Nutrient Absorption
>> 5. Potential Role in Weight Management
● Green Tea vs. Other Beverages for Digestive Health
● Comparison with Other Herbal Teas
● Incorporating Green Tea into Your Diet
● Additional Benefits of L-Theanine
>> Improved Cognitive Function
>> Cardiovascular Health
>> Immune System Support
● Cultural Significance of Green Tea
● Incorporating Green Tea into Daily Life
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the primary benefit of L-theanine for digestive health?
>> 2. How does green tea influence gut microbiota?
>> 3. Can L-theanine affect nutrient absorption?
>> 4. Is green tea easier to digest than coffee?
>> 5. What other health benefits does L-theanine offer?
● Citations:
Green tea, particularly its L-theanine content, has been extensively studied for its potential benefits on overall health, including digestive health. L-theanine, an amino acid found predominantly in green tea, is known for its calming effects and potential influence on various physiological processes. This article explores how green tea L-theanine, especially at a concentration of 60%, might impact digestive health.
Introduction to L-Theanine and Green Tea
L-theanine is a non-protein amino acid that contributes to the umami taste of green tea. It is known for its relaxing properties and is often used in dietary supplements to promote calmness and focus. Green tea, rich in L-theanine and other compounds like polyphenols and caffeine, has been a staple in many cultures for its health benefits.
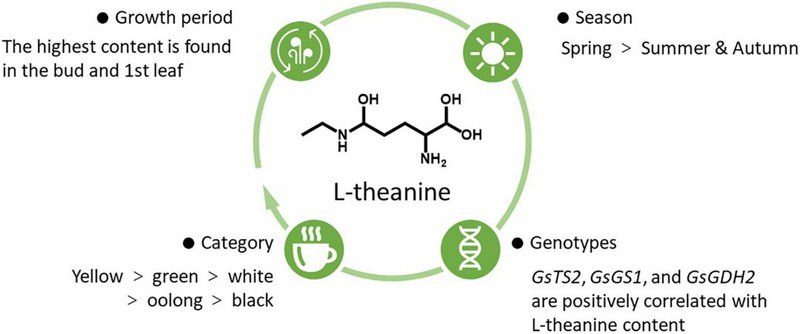
L-Theanine Structure and Properties
L-theanine, chemically known as N-ethyl-L-glutamine, is synthesized in the roots of tea plants and accumulates in the leaves. Its molecular formula is C7H14N2O3, with a molecular weight of 174.20 g/mol. The high purity of L-theanine, such as the 60% concentration offered by some supplements, ensures a potent formulation for various health benefits.
Impact of L-Theanine on Digestive Health
1. Relaxation and Stress Reduction
Stress can negatively impact digestion by slowing down the digestive process and exacerbating conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). L-theanine's calming effects can help reduce stress, potentially improving digestive efficiency. Studies have shown that individuals who consume L-theanine experience reduced cortisol levels, which can alleviate digestive discomfort associated with stress.
2. Modulation of Gut Microbiota
Green tea, including its L-theanine content, can influence the gut microbiota by promoting beneficial bacteria and inhibiting harmful ones. This modulation supports a healthy digestive system and aids in nutrient absorption. A balanced gut microbiome is crucial for maintaining a robust immune system and preventing digestive disorders.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
L-theanine and other green tea compounds have anti-inflammatory properties, which can soothe the digestive tract and alleviate symptoms of inflammatory conditions such as gastritis or colitis. These anti-inflammatory effects may also help reduce the risk of chronic diseases like cancer and cardiovascular disease.
4. Influence on Nutrient Absorption
Research suggests that L-theanine may affect nutrient absorption by modulating the transport of certain amino acids in the intestine. However, its impact on overall digestive health in this regard is still being studied. Further investigation is needed to understand how L-theanine influences nutrient uptake and utilization in the body.
5. Potential Role in Weight Management
L-theanine may also play a role in weight management by influencing metabolism and fat burning. While its direct impact on digestive health is less clear, maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of digestive disorders like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Green Tea vs. Other Beverages for Digestive Health
Green tea is often compared to coffee in terms of digestive impact. While coffee can be harsh on the stomach due to its acidity, green tea is generally easier to digest and may offer more sustained benefits for digestive health. Additionally, green tea's lower caffeine content compared to coffee means it is less likely to cause digestive discomfort or insomnia.
Comparison with Other Herbal Teas
Other herbal teas, such as peppermint and chamomile, are also known for their digestive benefits. Peppermint tea can help relieve symptoms of IBS, while chamomile tea promotes relaxation and may aid in reducing digestive stress. However, green tea's unique combination of L-theanine and polyphenols offers a broader range of health benefits.

Incorporating Green Tea into Your Diet
Incorporating green tea into your diet can be simple and beneficial. Drinking green tea regularly, either hot or cold, can provide a consistent intake of L-theanine and other beneficial compounds. Additionally, green tea can be used in cooking or as an ingredient in smoothies and desserts.
Additional Benefits of L-Theanine
Improved Cognitive Function
L-theanine is well-known for its ability to enhance cognitive function by promoting focus and concentration. This effect is particularly beneficial for individuals with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or those seeking to improve their mental clarity.
Cardiovascular Health
Green tea, including its L-theanine content, has been associated with improved cardiovascular health. The antioxidants in green tea may help reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering cholesterol levels and improving blood vessel function.
Immune System Support
L-theanine may also support immune function by enhancing the activity of certain immune cells. This can help protect against infections and diseases, contributing to overall health and well-being.
By incorporating green tea L-theanine into your diet, you can potentially experience these additional benefits alongside improved digestive health.
Cultural Significance of Green Tea
Green tea has been an integral part of many cultures, particularly in Asia, for centuries. In Japan, the traditional tea ceremony is a revered cultural practice that emphasizes mindfulness and respect for nature. Similarly, in China, green tea is often served at social gatherings and is considered a symbol of hospitality.
Incorporating Green Tea into Daily Life
Incorporating green tea into your daily routine can be simple and rewarding. Here are a few ways to enjoy green tea:
- Hot Green Tea: Perfect for cold mornings or as a relaxing evening drink.
- Iced Green Tea: Great for hot summer days, often served with lemon or mint.
- Green Tea Smoothies: Blend green tea with fruits and yogurt for a nutritious breakfast.
- Green Tea Infused Water: Add green tea leaves to a pitcher of water for a refreshing and healthy drink.
Conclusion
Green tea L-theanine, particularly at a concentration of 60%, offers several potential benefits for digestive health. Its ability to reduce stress, modulate gut microbiota, and exert anti-inflammatory effects can contribute to a healthier digestive system. However, more research is needed to fully understand its impact on nutrient absorption and overall digestive well-being.

FAQ
1. What is the primary benefit of L-theanine for digestive health?
L-theanine's primary benefit for digestive health is its ability to reduce stress, which can negatively impact digestion. By promoting relaxation, L-theanine may help improve digestive efficiency.
2. How does green tea influence gut microbiota?
Green tea, including its L-theanine content, can influence gut microbiota by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting harmful ones. This modulation supports a healthy digestive system.
3. Can L-theanine affect nutrient absorption?
Research indicates that L-theanine may modulate the absorption of certain nutrients, particularly amino acids, in the intestine. However, its overall impact on nutrient absorption is still under investigation.
4. Is green tea easier to digest than coffee?
Yes, green tea is generally easier to digest than coffee due to its lower acidity and potential anti-inflammatory effects, which can soothe the digestive tract.
5. What other health benefits does L-theanine offer?
L-theanine offers several health benefits beyond digestive health, including promoting relaxation, improving focus, supporting immune function, and potentially aiding in weight management.
Citations:
[1] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/324120
[2] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5546063/
[3] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8271705/
[4] https://www.marknature.com/products/green-tea-extract-60-l-theanine
[5] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2lGvni0PUeg
[6] https://www.cnet.com/health/nutrition/green-tea-hidden-benefits-focus-calmness-gut-health/
[7] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10179891/
[8] https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ptr.6277
[9] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9014247/
[10] https://globalnews.ca/video/10170817/the-kyle-files-insider-tips-on-l-theanine-and-digestive-wisdom
[11] https://www.davincilabs.com/l-theanine-60.html
[12] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cRo2V5cR4B4
[13] https://www.instagram.com/chanowa_australia/p/DGm3sa0AGgE/?locale=ar-en
[14] https://smartq.pureforyou.com/products/33055632883746/l-theanine-60
[15] https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-59383-y
[16] https://www.xiahepublishing.com/m/2472-0712/ERHM-2020-00048
[17] https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-54808-5
[18] https://calgaryneuropathy.com/60-l-theanine/






























