Content Menu
● The Composition of Green Tea Extract
>> Polyphenols
>> Caffeine
>> L-theanine
>> Vitamins and Minerals
● Potential Benefits of Green Tea Extract
>> Weight Loss Support
>> Antioxidant Protection
>> Heart Health
>> Brain Function
>> Skin Health
● How Green Tea Extract is Made
● Forms of Green Tea Extract
● Dosage and Safety Considerations
>> Recommended Dosage
>> Potential Side Effects
>> Caffeine Sensitivity
>> Interactions with Medications
>> Liver Health Considerations
● Choosing a Quality Green Tea Extract Supplement
● Green Tea Extract vs. Drinking Green Tea
● Incorporating Green Tea Extract into Your Routine
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> 1. Is green tea extract safe for everyone?
>> 2. How much caffeine is in green tea extract?
>> 3. Can green tea extract help with weight loss?
>> 4. How long does it take to see results from green tea extract?
>> 5. Can I take green tea extract if I'm sensitive to caffeine?
● Citations:
Green tea extract has gained significant popularity in recent years due to its potential health benefits. This concentrated form of green tea contains powerful compounds that may support weight loss, boost energy, and promote overall well-being. In this comprehensive article, we'll explore the components of green tea extract, its potential benefits, and important considerations for use.

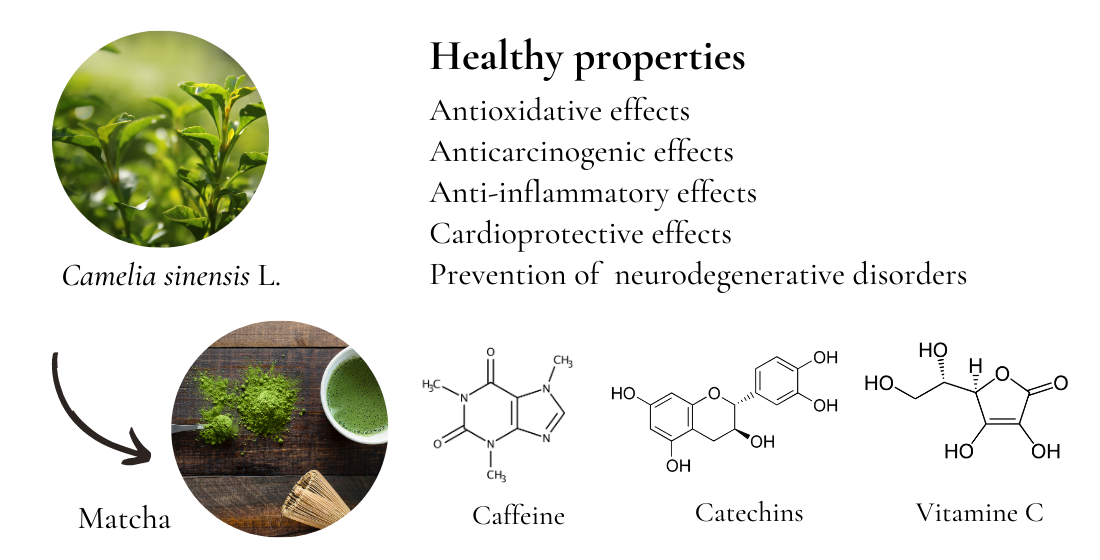
The Composition of Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract is derived from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant, the same plant used to make green tea beverages. However, the extract is a more concentrated form, containing higher levels of beneficial compounds. The main components of green tea extract include:
Polyphenols
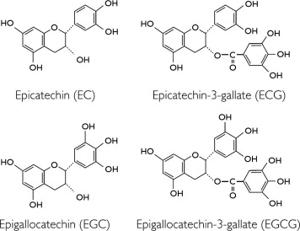
Polyphenols are a group of plant-based compounds with antioxidant properties. In green tea extract, the most abundant polyphenols are catechins. The primary catechins found in green tea extract are:
- Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)
- Epigallocatechin (EGC)
- Epicatechin gallate (ECG)
- Epicatechin (EC)
Among these, EGCG is the most abundant and well-studied catechin, believed to be responsible for many of the health benefits associated with green tea extract.
Caffeine
While green tea extract contains less caffeine than coffee, it still provides a mild stimulant effect. The caffeine content in green tea extract can vary, but it typically ranges from 2-4% of the extract's dry weight.
L-theanine
L-theanine is an amino acid found in tea leaves that may promote relaxation and reduce stress. It works synergistically with caffeine to provide a calm, focused energy without the jitters often associated with caffeine consumption.
Vitamins and Minerals
Green tea extract contains small amounts of various vitamins and minerals, including:
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin B complex
- Vitamin E
- Manganese
- Zinc
- Chromium
Potential Benefits of Green Tea Extract
Research suggests that green tea extract may offer numerous health benefits due to its rich composition of bioactive compounds. Some potential benefits include:
Weight Loss Support
Green tea extract may boost metabolism and increase fat burning, potentially aiding in weight loss efforts. The combination of caffeine and EGCG is thought to be responsible for these effects.
Antioxidant Protection
The high concentration of polyphenols in green tea extract provides potent antioxidant protection. These compounds help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases and supporting overall health.
Heart Health
Some studies suggest that green tea extract may support heart health by helping to lower cholesterol levels and improve blood flow. The polyphenols in green tea extract may also help reduce inflammation in the cardiovascular system.
Brain Function
The combination of caffeine and L-theanine in green tea extract may improve cognitive function, including attention, memory, and reaction time. Additionally, the antioxidants in green tea extract may protect brain cells from oxidative stress.
Skin Health
The antioxidants in green tea extract, particularly EGCG, may help protect the skin from UV damage and signs of aging. Some skincare products now incorporate green tea extract for its potential skin-protective properties.
How Green Tea Extract is Made
Green tea extract is typically produced through a multi-step process:
1. Harvesting: Fresh green tea leaves are harvested from the Camellia sinensis plant.
2. Steaming: The leaves are quickly steamed to prevent oxidation and preserve the beneficial compounds.
3. Drying: The steamed leaves are dried to remove moisture.
4. Extraction: The dried leaves are steeped in water or a water-alcohol solution to extract the beneficial compounds.
5. Concentration: The liquid extract is then concentrated through evaporation or other methods.
6. Powdering: The concentrated extract is often spray-dried to create a powder form.
7. Encapsulation: For supplement use, the powder is typically encapsulated or pressed into tablets.
Forms of Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract is available in various forms, including:
- Capsules
- Tablets
- Liquid extracts
- Powders
- Topical creams or lotions
The most common form for supplementation is capsules, which provide a convenient and standardized dose of green tea extract.
Dosage and Safety Considerations
While green tea extract is generally considered safe for most people when used as directed, it's important to consider the following:
Recommended Dosage
The appropriate dosage of green tea extract can vary depending on the specific product and intended use. However, many studies have used doses ranging from 300-800 mg of green tea extract per day. It's essential to follow the manufacturer's recommendations and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Potential Side Effects
Some people may experience side effects from green tea extract, particularly when consumed in high doses. Possible side effects include:
- Stomach upset
- Headache
- Insomnia
- Irritability
- Increased heart rate
- Dizziness
Caffeine Sensitivity
Individuals sensitive to caffeine should be cautious when using green tea extract, as it does contain caffeine. Decaffeinated green tea extract is available for those who wish to avoid caffeine.
Interactions with Medications
Green tea extract may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners, stimulants, and some antibiotics. It's crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before using green tea extract if you're taking any medications.
Liver Health Considerations
In rare cases, high doses of green tea extract have been associated with liver problems. Individuals with liver disease or a history of liver issues should consult a healthcare provider before using green tea extract supplements.
Choosing a Quality Green Tea Extract Supplement
When selecting a green tea extract supplement, consider the following factors:
1. Standardization: Look for products standardized to contain a specific percentage of polyphenols or EGCG.
2. Third-party testing: Choose supplements that have been tested by independent laboratories for purity and potency.
3. Reputable manufacturers: Select products from well-known, reputable supplement companies.
4. Form and dosage: Consider which form (capsules, liquid, etc.) and dosage best fits your needs and preferences.
5. Additional ingredients: Check the label for any additional ingredients or fillers that may not be necessary or desirable.
Green Tea Extract vs. Drinking Green Tea
While both green tea extract and brewed green tea offer health benefits, there are some key differences:
| Green Tea Extract | Brewed Green Tea |
| Higher concentration of polyphenols | Lower concentration of polyphenols |
| Convenient, standardized dosage | Variable polyphenol content depending on brewing method |
| May contain higher caffeine levels | Lower caffeine content |
| Can be taken as a supplement | Enjoyable beverage with additional hydration benefits |
| May have a higher risk of side effects | Generally well-tolerated with fewer side effects |
Incorporating Green Tea Extract into Your Routine
If you're interested in adding green tea extract to your wellness routine, consider these tips:
1. Start with a low dose and gradually increase as tolerated.
2. Take green tea extract with meals to minimize the risk of stomach upset.
3. Be consistent with your supplementation for best results.
4. Monitor your caffeine intake from all sources when using green tea extract.
5. Consider cycling your use of green tea extract, taking breaks periodically.
Conclusion
Green tea extract is a concentrated source of beneficial compounds found in green tea, particularly polyphenols like EGCG. These compounds may offer various health benefits, including support for weight management, heart health, and cognitive function. While generally safe for most people, it's important to use green tea extract responsibly and consult with a healthcare provider before adding it to your supplement regimen. By choosing a high-quality product and using it as directed, green tea extract can be a valuable addition to a healthy lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is green tea extract safe for everyone?
Green tea extract is generally safe for most adults when used as directed. However, some individuals may be more sensitive to its effects or experience side effects. It's always best to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking medications.
2. How much caffeine is in green tea extract?
The caffeine content in green tea extract can vary depending on the specific product and extraction process. Typically, green tea extract contains about 2-4% caffeine by weight. For a 500 mg capsule of green tea extract, this would translate to approximately 10-20 mg of caffeine. However, some products may be decaffeinated or have higher caffeine content, so it's important to check the label or contact the manufacturer for specific information.
3. Can green tea extract help with weight loss?
Some studies suggest that green tea extract may support weight loss efforts by boosting metabolism and increasing fat oxidation. The combination of caffeine and EGCG in green tea extract is thought to be responsible for these effects. However, it's important to note that green tea extract is not a magic solution for weight loss and should be used in conjunction with a healthy diet and regular exercise for best results.
4. How long does it take to see results from green tea extract?
The time it takes to see results from green tea extract can vary depending on the individual and the specific benefits you're looking for. Some people may notice increased energy or improved focus relatively quickly, while other potential benefits like weight loss or improvements in cholesterol levels may take several weeks or months of consistent use to become apparent. It's important to be patient and consistent with your supplementation, and to remember that individual results may vary.
5. Can I take green tea extract if I'm sensitive to caffeine?
If you're sensitive to caffeine, you may want to be cautious when using green tea extract, as it does contain caffeine. However, there are decaffeinated green tea extract supplements available that may be more suitable for caffeine-sensitive individuals. Additionally, the L-theanine in green tea extract may help to mitigate some of the potential side effects of caffeine. If you're concerned about caffeine sensitivity, it's best to start with a low dose of green tea extract and gradually increase as tolerated, or consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Citations:
[1] https://www.greentea.net/ingredients/
[2] https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=19&contentid=GreenTeaExtract
[3] https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/green-tea-extract.html
[4] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kmlcjBJ05Sk
[5] https://www.elo.health/articles/green-tea-extract-supplements/
[6] https://www.vumc.org/poison-control/toxicology-question-week/march-12-2021-what-are-adverse-effects-green-tea-extract
[7] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7600665/
[8] https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/herb/green-tea
[9] https://www.freepik.com/free-photos-vectors/green-tea-extract
[10] https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-960/green-tea
[11] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Green_tea
[12] https://www.zhounutrition.com/blogs/the-greatness-files/green-tea-extract-q-a






























