Content Menu
● Understanding Green Tea Extract
>> Key Components of Green Tea Extract
● How Green Tea Extract Affects Insulin Levels
>> Effects on Insulin Sensitivity
>> Mechanisms of Action
● Do Green Tea Extract Pills Spike Insulin?
>> Clinical Evidence
● Potential Benefits of Green Tea Extract for Diabetics
● Additional Health Benefits of Green Tea Extract
● Safety and Side Effects
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the recommended dosage of green tea extract?
>> 2. Can I take green tea extract if I am diabetic?
>> 3. Are there any side effects associated with green tea extract?
>> 4. How does green tea extract compare to regular green tea?
>> 5. Can I consume green tea extract while taking diabetes medication?
● Citations:
Green tea has long been celebrated for its numerous health benefits, particularly in relation to metabolic health. Among these benefits, the impact of green tea extract (GTE) on insulin levels and blood sugar regulation has garnered significant attention. This article will explore whether green tea extract pills spike insulin levels, how they influence insulin sensitivity, and their overall effect on blood sugar control.
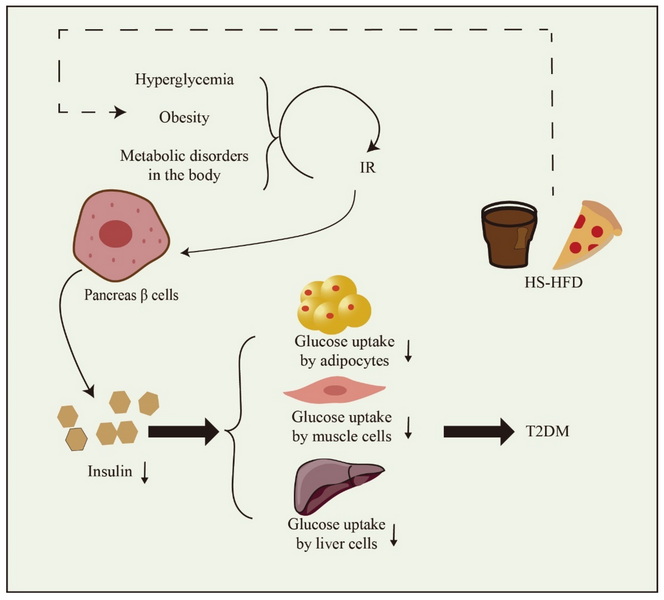
Understanding Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract is derived from the leaves of the *Camellia sinensis* plant and is rich in polyphenols, particularly catechins like epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). These compounds are believed to contribute to various health benefits, including antioxidant effects, weight loss, and improved metabolic function.
Key Components of Green Tea Extract
- Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG): The most abundant catechin in green tea, known for its potential health benefits.
- Caffeine: Present in smaller amounts, caffeine may also play a role in metabolic processes.
- Other Catechins: Includes epicatechin (EC), epicatechin gallate (ECG), and gallocatechin gallate (GCG).
How Green Tea Extract Affects Insulin Levels
Research indicates that green tea extract can influence insulin sensitivity and blood sugar levels, but the results are complex and sometimes contradictory.
Effects on Insulin Sensitivity
Several studies have shown that GTE may actually improve insulin sensitivity rather than spike insulin levels. For instance:
- A study involving individuals with type 2 diabetes found that taking 500 mg of GTE three times daily significantly improved insulin resistance after 16 weeks.
- Another study reported that participants consuming green tea extract experienced lower fasting blood glucose levels compared to those taking a placebo.
Mechanisms of Action
The beneficial effects of GTE on insulin sensitivity can be attributed to several mechanisms:
- Inhibition of Amylase: Green tea catechins inhibit the enzyme amylase, which breaks down carbohydrates into glucose. This inhibition can reduce the amount of glucose entering the bloodstream after meals.
- Enhanced GLP-1 Production: Some studies suggest that GTE may increase levels of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), a hormone that enhances insulin secretion and reduces blood sugar levels.
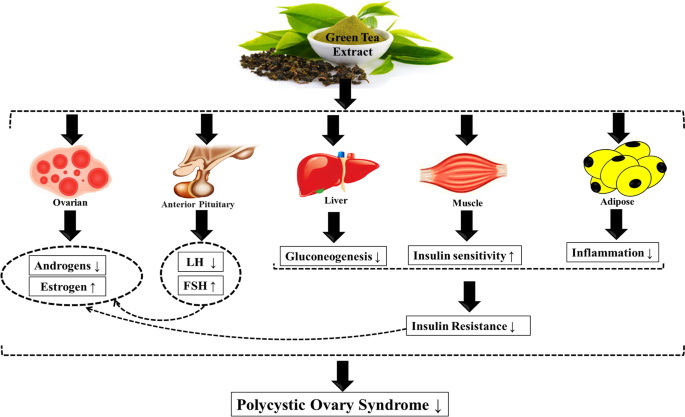
Do Green Tea Extract Pills Spike Insulin?
The evidence suggests that green tea extract does not spike insulin levels; rather, it may help regulate them.
Clinical Evidence
1. Clinical Trials: In clinical trials involving individuals with type 2 diabetes, GTE supplementation led to improvements in glycemic control without significant increases in insulin levels.
2. Meta-Analyses: A meta-analysis indicated that GTE consumption resulted in decreased fasting insulin concentrations among participants.
3. Animal Studies: Research on mice has shown that EGCG can reduce blood sugar spikes after carbohydrate consumption by improving glucose metabolism.
Potential Benefits of Green Tea Extract for Diabetics
For individuals managing diabetes or prediabetes, incorporating green tea extract into their regimen may offer several advantages:
- Lowering Blood Sugar Levels: Regular consumption of GTE has been associated with lower fasting blood glucose and hemoglobin A1c levels.
- Improving Gut Health: Recent studies have also linked GTE to improved gut health by reducing inflammation and "leaky gut," which can further aid in regulating blood sugar levels.
Additional Health Benefits of Green Tea Extract
Beyond its effects on insulin and blood sugar regulation, green tea extract offers a range of other health benefits:
- Weight Management: Green tea extract is often marketed as a weight loss aid due to its potential to increase metabolic rate and fat oxidation. Studies suggest that it may enhance fat burning during exercise and at rest.
- Cardiovascular Health: The antioxidants in green tea extract can help lower LDL cholesterol levels and improve overall heart health by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Cancer Prevention: Some research indicates that the polyphenols in green tea may have protective effects against certain types of cancer by inhibiting tumor growth and promoting apoptosis (cell death) in cancer cells.
- Cognitive Function: The caffeine and L-theanine present in green tea may improve brain function by enhancing attention, memory, and mood. Some studies suggest that regular consumption could lower the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's.
Safety and Side Effects
While green tea extract is generally considered safe for most people when taken at recommended doses, there are some potential side effects to be aware of:
- Liver Toxicity: High doses of green tea extract have been linked to rare cases of liver damage. Symptoms can include jaundice, nausea, and abdominal pain. Individuals with pre-existing liver conditions should consult a healthcare provider before using GTE supplements.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Some people may experience nausea, diarrhea, or stomach upset when taking green tea extract, especially on an empty stomach.
- Caffeine Sensitivity: Due to its caffeine content, individuals sensitive to caffeine may experience anxiety, insomnia, or increased heart rate when consuming green tea extract.
Conclusion
In conclusion, green tea extract pills do not spike insulin levels; instead, they appear to enhance insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar levels. The active compounds in green tea work through various mechanisms to support metabolic health. Additionally, GTE offers a range of other health benefits including weight management, cardiovascular support, cancer prevention, and cognitive enhancement. However, it is essential for individuals considering GTE supplements to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure safety and effectiveness tailored to their specific health needs.
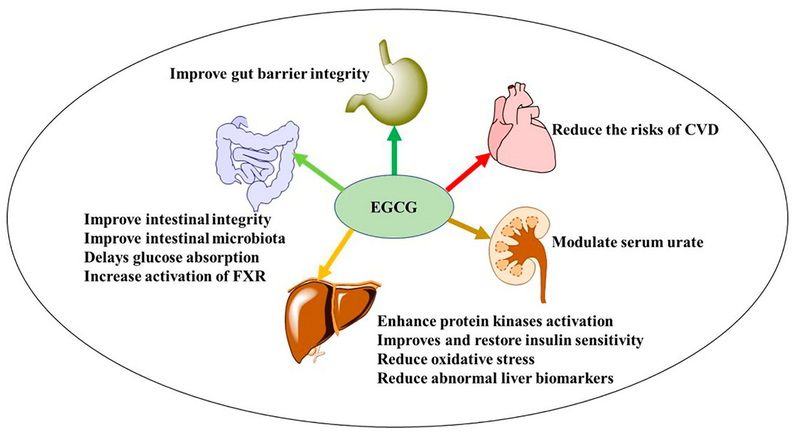
FAQ
1. What is the recommended dosage of green tea extract?
The typical dosage ranges from 250 mg to 500 mg per day, depending on individual health goals and product formulations.
2. Can I take green tea extract if I am diabetic?
Yes, many studies suggest that green tea extract can be beneficial for individuals with diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity and lowering blood sugar levels.
3. Are there any side effects associated with green tea extract?
While generally safe for most people when taken at recommended doses, high doses may lead to liver toxicity or gastrointestinal issues.
4. How does green tea extract compare to regular green tea?
Green tea extract contains higher concentrations of catechins compared to brewed green tea, making it more potent for certain health benefits.
5. Can I consume green tea extract while taking diabetes medication?
It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before combining green tea extract with diabetes medications to avoid potential interactions.
Citations:
[1] https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0091163
[2] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24206044/
[3] https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=19&contentid=greenteaextract
[4] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38031409/
[5] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10218622/
[6] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11596636/
[7] https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-960/green-tea
[8] https://hsph.harvard.edu/news/green-tea-healthy-habit/
[9] https://www.rupahealth.com/post/the-role-of-green-tea-extract-in-metabolic-syndrome-management
[10] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/269538
[11] https://health.clevelandclinic.org/green-tea-extract-a-better-way-to-boost-energy-or-not
[12] https://www.vumc.org/poison-control/toxicology-question-week/march-12-2021-what-are-adverse-effects-green-tea-extract
[13] https://www.e-dmj.org/journal/view.php?doi=10.4093%2Fdmj.2017.41.4.251
[14] https://www.nytimes.com/2024/09/24/well/green-tea-weight-loss-ozempic.html
[15] https://ajcn.nutrition.org/article/S0002-9165(23)05180-8/fulltext
[16] https://www.ars.usda.gov/research/publications/publication/?seqNo115=218115
[17] https://www.ars.usda.gov/research/publications/publication/?seqNo115=208910
[18] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242333194_Effect_of_green_tea_on_glucose_control_and_insulin_sensitivity_A_meta-analysis_of_17_randomized_controlled_trials
[19] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/top-10-evidence-based-health-benefits-of-green-tea
[20] https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/green-tea
[21] https://health.clevelandclinic.org/green-tea-health-benefits
[22] https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/herb/green-tea
[23] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-benefits-of-green-tea-extract
[24] https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-76714/green-tea-leaf-extract-oral/details
[25] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3689013/
[26] https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/nutrition/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022.1084455/full






























