Content Menu
● Understanding Uterine Fibroids
>> Types of Fibroids
● The Role of Green Tea Extract
>> Mechanisms of Action
● Research Findings
● Recommended Dosage
>> Supplementation Considerations
● Combining Treatments
● Lifestyle Factors
● Foods That May Help Manage Fibroids
>> Foods To Avoid
● Patient Experiences
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What are uterine fibroids?
>> 2. How does green tea extract help with fibroids?
>> 3. What is the recommended dosage of green tea extract for shrinking fibroids?
>> 4. Can I take green tea extract with other medications?
>> 5. Are there any side effects associated with taking green tea extract?
● Citations:
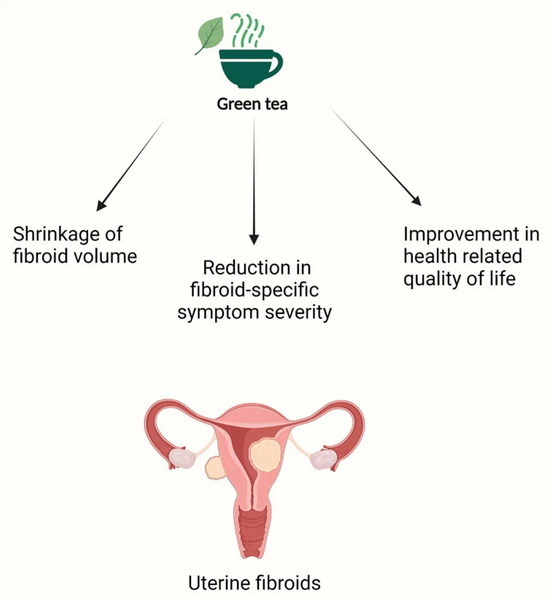
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are benign tumors that can cause a range of symptoms, including heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and complications during pregnancy. These growths are common among women, especially those of African descent, with studies indicating that up to 80% of women will develop fibroids by the age of 50. While traditional treatments have included surgical options, recent research has explored the potential of natural remedies, particularly green tea extract, in managing fibroid symptoms and size.
Understanding Uterine Fibroids
Fibroids are non-cancerous tumors composed of smooth muscle cells and fibrous connective tissue. They can vary in size from small seedlings to large masses that can distort the uterus. The exact cause of fibroids is not fully understood, but they are believed to be influenced by hormonal factors, particularly estrogen.
Types of Fibroids
- Subserosal Fibroids: These grow on the outer wall of the uterus and can protrude into the pelvic cavity.
- Intramural Fibroids: The most common type, these develop within the muscular wall of the uterus.
- Submucosal Fibroids: These grow just beneath the lining of the uterus and can protrude into the uterine cavity.
- Pedunculated Fibroids: These are attached to the uterus by a stalk and can be either subserosal or submucosal.
The Role of Green Tea Extract
Green tea is rich in polyphenols, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which has been shown to possess antioxidant properties. Research indicates that EGCG may inhibit the growth of fibroid cells by affecting various biochemical pathways involved in cell proliferation.
Mechanisms of Action
1. Reduction of Cell Division: EGCG has been found to lower levels of cyclin D1, a protein that promotes cell division.
2. Impact on Extracellular Matrix: It reduces levels of fibronectin, a key protein in the extracellular matrix that supports fibroid structure.
3. Disruption of Growth Pathways: EGCG interferes with signaling pathways that contribute to fibroid growth and maintenance.
Research Findings
Recent studies have provided promising results regarding the use of green tea extract for managing uterine fibroids:
- A study conducted at Johns Hopkins University revealed that treatment with EGCG significantly reduced fibroid cell growth in laboratory settings.
- A clinical trial involving 39 women showed that daily consumption of 800 mg of green tea extract (containing 45% EGCG) led to a 32.6% reduction in total fibroid volume over four months compared to a placebo group.
- Another study indicated that a combination of EGCG with vitamin D resulted in significant reductions in fibroid size among women aged 40 and older.
Recommended Dosage
Based on current research, the recommended dosage for green tea extract to effectively shrink fibroids is approximately:
- 800 mg per day: This is typically equivalent to consuming between 5 to 10 cups of green tea daily, depending on the concentration of EGCG in each cup (which generally ranges from 50 to 100 mg per cup).
Supplementation Considerations
For those who find it challenging to consume large quantities of green tea, supplementation with concentrated green tea extract may be a more practical option. When choosing supplements, it is crucial to look for products standardized to contain at least 45% EGCG.
Combining Treatments
In addition to green tea extract, some studies suggest that combining it with vitamin D may enhance its effectiveness against fibroids. Vitamin D has been linked to improved reproductive health and may play a role in regulating cell growth. A study indicated that women taking both vitamin D and green tea extract experienced a significant reduction in mean fibroid size compared to those taking a placebo.
Lifestyle Factors
Incorporating lifestyle changes can also support overall health and potentially mitigate fibroid symptoms:
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help manage symptoms. Foods high in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties may be particularly beneficial.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity may help regulate hormones and reduce stress levels. Exercise has been shown to improve overall health and may aid in weight management, which is crucial since obesity is a risk factor for fibroid development.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga and meditation can support mental well-being. Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that may exacerbate fibroid symptoms.
Foods That May Help Manage Fibroids
Certain dietary choices may help manage symptoms or potentially reduce the growth of uterine fibroids:
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, kale, and cabbage contain compounds that help detoxify excess estrogen from the body.
- Fruits: Berries and citrus fruits are rich in antioxidants which may help reduce inflammation.
- Healthy Fats: Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish like salmon or flaxseeds may help balance hormones.
- Legumes: Beans and lentils provide fiber and nutrients that support overall health.
Foods To Avoid
Certain foods may exacerbate symptoms associated with uterine fibroids:
- High-Sugar Foods: Refined sugars can lead to insulin spikes which may promote fibroid growth.
- Processed Foods: These often contain unhealthy fats and additives that could negatively impact hormonal balance.
- Alcohol: Excessive consumption can disrupt hormonal balance and exacerbate symptoms.
Patient Experiences
Many women have reported positive outcomes after incorporating green tea extract into their daily regimen. Some have noted improvements not only in symptom severity but also in overall well-being. Testimonials highlight how consistent use led to reduced menstrual pain and lighter periods.
Conclusion
The potential for green tea extract to shrink uterine fibroids presents an exciting avenue for non-surgical treatment options. While current research shows promising results regarding its efficacy—especially when combined with vitamin D—further studies are needed to confirm these findings across diverse populations and age groups.
Women considering this approach should consult healthcare professionals before starting any new treatment regimen. Individual responses may vary based on specific health conditions and other factors.
FAQ
1. What are uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous tumors made up of smooth muscle cells and connective tissue that grow in or on the uterus.
2. How does green tea extract help with fibroids?
Green tea extract contains EGCG, which may inhibit cell division and reduce growth factors associated with fibroid development.
3. What is the recommended dosage of green tea extract for shrinking fibroids?
The recommended dosage is approximately 800 mg per day, which is equivalent to consuming about 5 to 10 cups of green tea daily.
4. Can I take green tea extract with other medications?
It is essential to consult a healthcare provider before combining green tea extract with other medications or supplements to avoid potential interactions.
5. Are there any side effects associated with taking green tea extract?
While generally safe for most people when consumed in moderation, high doses may lead to side effects such as stomach upset or liver issues; thus, moderation is key.
Citations:
[1] https://pure.johnshopkins.edu/en/publications/fibroids-and-unexplained-infertility-treatment-with-epigallocatec
[2] https://www.nichd.nih.gov/newsroom/news/080723-uterine-fibroids-green-tea
[3] https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/6/1439
[4] https://www.medparkhospital.com/en-US/lifestyles/uterine-fibroids-what-should-be-avoided
[5] https://www.gafibroids.com/patient-resources/fibroid-diet/
[6] https://fibroids.com/blog/food-fibroids-follow-diet-plan/
[7] https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2023/07/230712124611.htm
[8] https://www.contemporaryobgyn.net/view/vitamin-d-and-green-tea-extract-for-treatment-of-uterine-fibroids
[9] https://www.healthline.com/health/fibroids-diet
[10] https://fibroidexpert.com/blog/what-foods-can-help-reduce-uterine-fibroids/






























