Content Menu
● Understanding Vitamin K
● Vitamin K Content in Green Tea
● Vitamin K Content in Grapeseed Extract
● Health Benefits of Green Tea and Grapeseed Extract
>> Green Tea Benefits
>> Grapeseed Extract Benefits
● Considerations for Consumption
>> Green Tea
>> Grapeseed Extract
● Combining Green Tea and Grapeseed Extract
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. Can green tea or grapeseed extract replace dietary sources of vitamin K?
>> 2. Are there any risks associated with consuming too much green tea or grapeseed extract?
>> 3. How do the antioxidants in green tea and grapeseed extract benefit health?
>> 4. Can green tea or grapeseed extract interfere with blood-thinning medications?
>> 5. Is it safe to combine green tea and grapeseed extract supplements?
● Citations:
Green tea and grapeseed extracts are popular dietary supplements known for their potential health benefits. While both are rich in various antioxidants and bioactive compounds, their vitamin K content is often a subject of interest. This article will explore the vitamin K content in green tea and grapeseed extracts, their potential health benefits, and considerations for consumption.
Understanding Vitamin K
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in blood clotting and bone metabolism. There are two main forms of vitamin K:
1. Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone): Found primarily in leafy green vegetables
2. Vitamin K2 (menaquinones): Produced by bacteria in the gut and found in some fermented foods
Vitamin K Content in Green Tea
Green tea is derived from the leaves of Camellia sinensis and is known for its high concentration of polyphenols, particularly catechins. While green tea is not typically considered a significant source of vitamin K, it does contain small amounts.
The vitamin K content in green tea can vary depending on factors such as:
- Tea variety
- Growing conditions
- Processing methods
- Brewing time and temperature
On average, a cup (240 ml) of brewed green tea contains approximately 0.1 to 0.3 micrograms (μg) of vitamin K[1]. This amount is relatively low compared to the recommended daily intake of vitamin K, which is:
- 120 μg for adult men
- 90 μg for adult women
It's important to note that the vitamin K content in green tea is primarily in the form of vitamin K1 (phylloquinone).
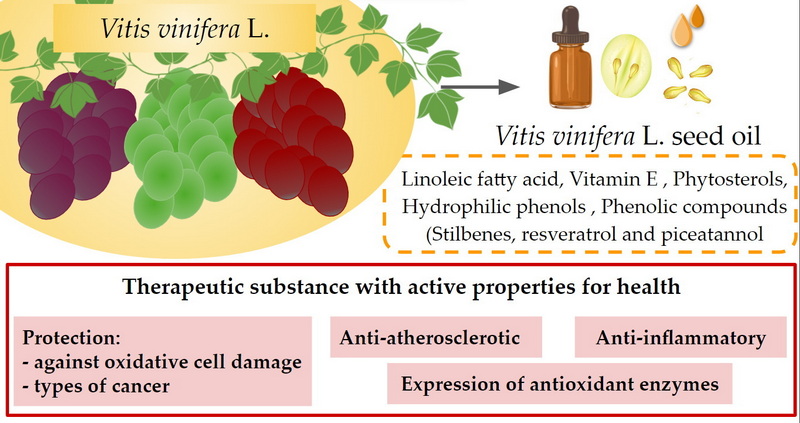
Vitamin K Content in Grapeseed Extract
Grapeseed extract is derived from the seeds of grapes and is known for its high concentration of proanthocyanidins, which are powerful antioxidants. Unlike green tea, grapeseed extract is not a significant source of vitamin K.
The vitamin K content in grapeseed extract is negligible, with most sources reporting no detectable amounts. This is because vitamin K is primarily found in the leafy parts of plants rather than seeds.
Health Benefits of Green Tea and Grapeseed Extract
While the vitamin K content in these supplements may be low, both green tea and grapeseed extract offer numerous potential health benefits due to their rich antioxidant profiles.
Green Tea Benefits
1. Antioxidant properties: Green tea is rich in catechins, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which has potent antioxidant effects[3].
2. Potential cancer prevention: Some studies suggest that the antioxidants in green tea may help reduce the risk of certain types of cancer.
3. Heart health: Regular consumption of green tea has been associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease.
4. Weight management: Green tea may boost metabolism and aid in weight loss efforts.
5. Brain function: The caffeine and L-theanine in green tea can improve cognitive performance and mood.
Grapeseed Extract Benefits
1. Powerful antioxidant: Grapeseed extract is rich in proanthocyanidins, which have strong antioxidant properties[1].
2. Cardiovascular health: Studies suggest that grapeseed extract may help lower blood pressure and improve blood flow.
3. Skin health: The antioxidants in grapeseed extract may help protect the skin from damage and improve overall skin appearance.
4. Cognitive function: Some research indicates that grapeseed extract may have neuroprotective effects and could potentially benefit cognitive function.
5. Anti-inflammatory properties: Grapeseed extract has shown promise in reducing inflammation in the body.

Considerations for Consumption
While green tea and grapeseed extract are generally considered safe for most people, there are some considerations to keep in mind:
Green Tea
- Caffeine content: Green tea contains caffeine, which may cause side effects in sensitive individuals or if consumed in large amounts.
- Interactions with medications: The caffeine and catechins in green tea may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners and some antibiotics.
- Iron absorption: Green tea may inhibit iron absorption, so it's best to consume it between meals if you're concerned about iron intake.
Grapeseed Extract
- Blood-thinning effects: Grapeseed extract may have mild blood-thinning properties, which could be a concern for people taking blood-thinning medications or those with bleeding disorders[1].
- Allergies: Individuals with grape allergies should avoid grapeseed extract.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: There is limited research on the safety of grapeseed extract during pregnancy and breastfeeding, so it's best to consult with a healthcare provider before use.
Combining Green Tea and Grapeseed Extract
Some people choose to combine green tea and grapeseed extract to maximize potential health benefits. While there is no specific research on the synergistic effects of these supplements, their complementary antioxidant profiles may offer enhanced protection against oxidative stress.
When combining these supplements, it's important to:
1. Follow recommended dosages for each supplement
2. Be aware of potential interactions with medications
3. Monitor for any adverse effects
4. Consult with a healthcare provider, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions
Conclusion
While green tea and grapeseed extract are not significant sources of vitamin K, they offer a wide range of potential health benefits due to their rich antioxidant content. Green tea contains small amounts of vitamin K1, while grapeseed extract has negligible vitamin K content. Both supplements are valued for their antioxidant properties and potential positive effects on cardiovascular health, cognitive function, and overall well-being.
When considering the use of these supplements, it's important to be aware of potential interactions and side effects, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking medications. As with any dietary supplement, it's always best to consult with a healthcare provider before adding green tea or grapeseed extract to your routine.

FAQ
1. Can green tea or grapeseed extract replace dietary sources of vitamin K?
No, green tea and grapeseed extract should not be relied upon as significant sources of vitamin K. To meet your vitamin K needs, it's important to consume a balanced diet that includes leafy green vegetables, which are rich in vitamin K1, and fermented foods, which provide vitamin K2.
2. Are there any risks associated with consuming too much green tea or grapeseed extract?
While both supplements are generally safe when consumed in moderation, excessive intake can lead to side effects. For green tea, high consumption may cause caffeine-related symptoms such as insomnia, nervousness, and increased heart rate. Grapeseed extract, when taken in very high doses, may cause headaches, dizziness, or nausea. Always follow recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare provider if you have concerns.
3. How do the antioxidants in green tea and grapeseed extract benefit health?
The antioxidants in green tea and grapeseed extract, such as catechins and proanthocyanidins, help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. This protection may contribute to reduced inflammation, improved cardiovascular health, and potential cancer prevention. Additionally, these antioxidants may support cognitive function and skin health.
4. Can green tea or grapeseed extract interfere with blood-thinning medications?
Both green tea and grapeseed extract have the potential to interact with blood-thinning medications. Green tea contains vitamin K, which can affect blood clotting, while grapeseed extract may have mild blood-thinning properties. If you're taking blood thinners or have a bleeding disorder, it's crucial to consult with your healthcare provider before using these supplements.
5. Is it safe to combine green tea and grapeseed extract supplements?
While there is no specific research on the combination of green tea and grapeseed extract supplements, many people choose to use both for their complementary antioxidant profiles. However, it's important to follow recommended dosages for each supplement and be aware of potential interactions with medications. As with any new supplement regimen, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before combining these supplements, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions.
Citations:
[1] https://aakp.org/ask-the-doc-grape-seed-extract-and-green-tea/
[2] https://patents.google.com/patent/CN104168772A/zh
[3] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7670682/
[4] http://cgmj.cgu.edu.tw/3501/350104.pdf
[5] https://digital.csic.es/bitstream/10261/88226/1/Effects_of_dietary_grape_seed_extract_on_growth_performance,.pdf
[6] https://benjamins.com/online/target/articles/target.18036.zhe.zh
[7] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/grape-seed-extract-benefits
[8] https://www.goldenagri.com.sg/cn/vitamin-a-101-more-than-meets-the-eye/






























