Content Menu
● Introduction to Cinnamon Zeylanicum
>> Origin and Production
● Health Benefits of Cinnamon Zeylanicum Bark Extract and Powder
>> Blood Sugar Management
>> Digestive Health
>> Antioxidant Properties
>> Anti-Inflammatory Effects
>> Cardiovascular Health
>> Antimicrobial Properties
>> Neuroprotective Effects
>> Wound Healing
● Culinary Uses of Cinnamon Zeylanicum
>> Traditional Uses
● Safety and Side Effects
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> 1. What is the difference between Ceylon cinnamon and Cassia cinnamon?
>> 2. Can Cinnamon Zeylanicum help with weight loss?
>> 3. Is Cinnamon Zeylanicum safe for people with diabetes?
>> 4. How does Cinnamon Zeylanicum compare to other antioxidants?
>> 5. Can Cinnamon Zeylanicum be used in cooking and baking?
● Citations:
Cinnamon Zeylanicum, commonly known as Ceylon cinnamon, is renowned for its rich flavor and aroma, as well as its numerous health benefits. The bark of this tree is used to produce both extract and powder forms, which are utilized in culinary and medicinal applications. In this article, we will delve into the benefits of Cinnamon Zeylanicum bark extract and powder, exploring their potential health advantages and uses.
Introduction to Cinnamon Zeylanicum
Cinnamon Zeylanicum is native to Sri Lanka and parts of India. It is considered "true cinnamon" due to its superior quality and lower coumarin content compared to other types of cinnamon, such as Cassia cinnamon. The lower coumarin levels make Ceylon cinnamon safer for consumption in larger quantities over time.
Origin and Production
Sri Lanka is the world's largest producer and exporter of Ceylon cinnamon, accounting for about 90% of the global market. The unique quality, color, flavor, and aroma of Ceylon cinnamon have earned it a long-standing reputation in the international market.
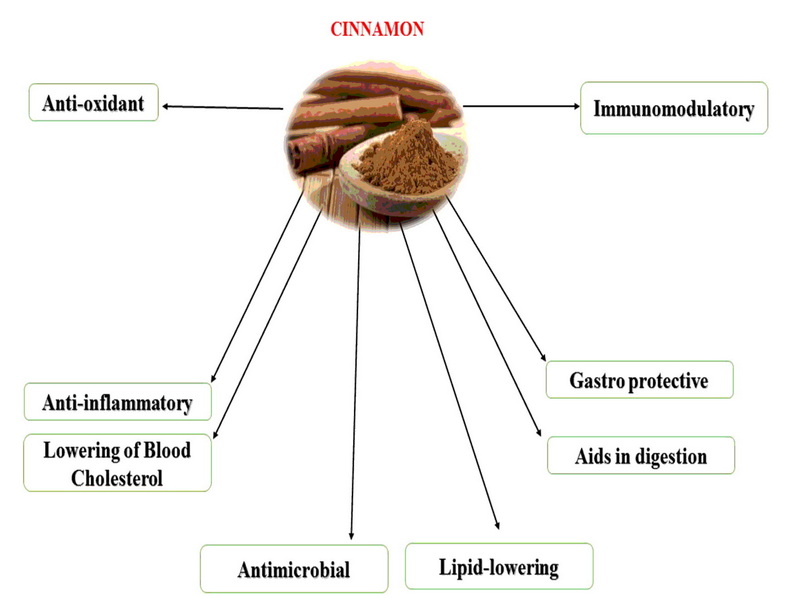
Health Benefits of Cinnamon Zeylanicum Bark Extract and Powder
Cinnamon Zeylanicum bark extract and powder have been studied for their potential health benefits, including:
Blood Sugar Management
Cinnamon has been extensively researched for its role in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Studies suggest that it may help improve insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, which can be beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes. For instance, a clinical trial showed that cinnamon intake significantly reduced fasting serum glucose, triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, and total cholesterol levels in people with type 2 diabetes[7].
Digestive Health
Traditionally, cinnamon is used as a digestive aid in Ayurvedic and Chinese medicine. It may help alleviate symptoms of indigestion and improve overall digestive health. Cinnamon's anti-inflammatory properties can also help relieve digestive symptoms caused by stress, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and colitis[1].
Antioxidant Properties
Cinnamon contains antioxidants like cinnamaldehyde, which can neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. This helps maintain a healthy balance in the body and reduces stress on the heart and other organs[3].
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Cinnamaldehyde in Ceylon cinnamon may also have anti-inflammatory properties, which could help reduce symptoms of chronic conditions like arthritis and heart disease[1].
Cardiovascular Health
Some studies suggest that cinnamon may help manage cholesterol levels and blood pressure, contributing to overall cardiovascular health. It appears to lower LDL and overall cholesterol levels without affecting HDL cholesterol significantly[1].
Antimicrobial Properties
Cinnamon has been known for its antimicrobial properties, which can help fight off bacterial and fungal infections. This makes it useful in traditional medicine for treating various infections[2][3].
Neuroprotective Effects
Cinnamon Zeylanicum may help prevent Alzheimer's disease by reducing tau aggregation and filament formation, which are hallmarks of the disease[5]. Additionally, its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in the brain may protect against other neurodegenerative disorders.
Wound Healing
Ceylon cinnamon has been studied for its wound healing properties. An experiment on rats showed that cinnamon extract accelerated the wound healing process and increased epithelialization compared to control groups[7].

Culinary Uses of Cinnamon Zeylanicum
Cinnamon Zeylanicum is widely used in baking, cooking, and as a flavoring agent in beverages. Its distinctive flavor and aroma make it a popular ingredient in many cuisines. In baking, cinnamon is often used in cakes, cookies, and pastries to add a warm, comforting flavor and aroma[4].
Traditional Uses
In addition to its culinary uses, cinnamon has a long history of medicinal use. It has been used as a neuroprotective agent and for the treatment of diabetes, inflammation, gastrointestinal disorders, and urinary infections[2].
Safety and Side Effects
Ceylon cinnamon is generally considered safe due to its low coumarin content. However, it is important to consume it in moderation as part of a balanced diet. High doses or long-term use of cinnamon supplements may be harmful[4].
Conclusion
Cinnamon Zeylanicum bark extract and powder offer a range of health benefits, from blood sugar management to anti-inflammatory effects. Its culinary uses are diverse, and it is considered safer than other types of cinnamon due to its low coumarin content. As research continues, the potential of Ceylon cinnamon as a natural health aid becomes increasingly evident.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between Ceylon cinnamon and Cassia cinnamon?
Ceylon cinnamon (Cinnamon Zeylanicum) is considered "true cinnamon" and has a lower coumarin content compared to Cassia cinnamon, making it safer for consumption in larger quantities.
2. Can Cinnamon Zeylanicum help with weight loss?
While some studies suggest that cinnamon may aid in weight management by improving insulin sensitivity and lipid profiles, there is no conclusive evidence that it directly promotes significant weight loss.
3. Is Cinnamon Zeylanicum safe for people with diabetes?
Cinnamon Zeylanicum may help manage blood sugar levels, but it should not replace medical treatment. Individuals with diabetes should consult their healthcare provider before using cinnamon as a supplement.
4. How does Cinnamon Zeylanicum compare to other antioxidants?
Cinnamon contains antioxidants like cinnamaldehyde, which are effective in neutralizing free radicals. However, its antioxidant capacity compared to other sources can vary based on the specific extract or preparation.
5. Can Cinnamon Zeylanicum be used in cooking and baking?
Yes, Cinnamon Zeylanicum is widely used in culinary applications due to its distinctive flavor and aroma. It is a popular ingredient in baking, cooking, and as a flavoring agent in beverages.
Citations:
[1] https://www.webmd.com/diet/health-benefits-ceylon-cinnamon
[2] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4586554/
[3] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3854496/
[4] https://www.pureleven.com/cinnamon-types-benefits-and-culinary-uses/
[5] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4003790/
[6] https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/14/15/6554
[7] https://consensus.app/home/blog/health-benefits-of-ceylon-cinnamon/
[8] https://nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ppp3.10192






























