Content Menu
● Introduction to Green Tea Polyphenols
>> Types of Catechins in Green Tea
● Factors Influencing Polyphenol Concentration
>> Solvent Concentration Impact on Extraction Yield
● Comparison with Other Teas
>> Antioxidant Activity Comparison
● Health Benefits Associated with High-Polyphenolic Green Tea Extracts
>> Cardiovascular Health Support
>> Anticancer Properties
>> Neuroprotective Effects
>> Weight Management
>> Metabolic Health
>> Potential Risks and Side Effects
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> 1. What Are Polyhenolics?
>> 2. How Do Extraction Methods Affect Yield?
>> 3. Why Is EGCG Important?
>> 4. Can I Increase My Intake Safely?
>> 5. Does Steeping Time Matter?
● Citations:
Green tea, known scientifically as Camellia sinensis, is renowned for its high content of polyphenols, which are compounds that act as natural antioxidants. These antioxidants play a crucial role in protecting the body against free radicals and oxidative stress, contributing to various health benefits. The concentration of polyphenols in green tea extracts can vary significantly based on factors such as extraction methods and solvent concentrations.
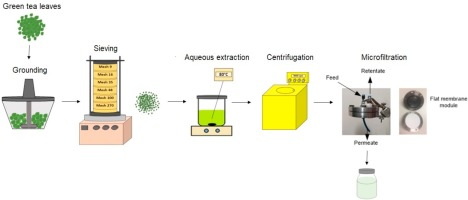
Introduction to Green Tea Polyphenols
Green tea contains a variety of polyphenolic compounds, with catechins being the most abundant. Among these catechins, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is the most prevalent and has been extensively studied for its potential health benefits. The total polyphenol content in green tea typically accounts for about 30% of its dry weight.
Types of Catechins in Green Tea
1. Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG): This is the most abundant catechin in green tea, known for its strong antioxidant properties.
2. Epicatechin Gallate (ECG): Another significant component with antioxidant capabilities.
3. Epigallocatechin (EGC): Known for its antioxidant activity.
4. Epicatechin (EC): Also contributes to the overall antioxidant capacity.
Factors Influencing Polyphenol Concentration
The concentration of polyphenols in green tea extracts can be influenced by several factors:
- Extraction Method: Techniques like maceration, microwave-assisted extraction, or ultrasound-assisted extraction can affect how much polyphenol is extracted from the leaves.
- Solvent Concentration: Ethanol-water mixtures are commonly used; varying ethanol concentrations can impact extract yield and quality.
- Steeping Time and Temperature: Longer steeping times at higher temperatures may increase infusion but could also lead to degradation if not controlled properly.
Solvent Concentration Impact on Extraction Yield
A study comparing ethanol-water solvent concentrations found that a 50% ethanol concentration yielded the highest total polyphenol content compared to 30% or 70% concentrations. This suggests that optimizing solvent composition is crucial for maximizing extract quality.
Comparison with Other Teas
Green tea generally contains more polyphenols than black or oolong teas due to differences in processing methods—green tea undergoes minimal processing compared to others like black or oolong teas which involve fermentation processes that reduce their phenolic content.
| Tea Type | Total Polyphenolic Content |
| White Tea | Maximum due to least processing |
| Green Tea | Higher than black but less than white |
| Black/Oolong | Lower due to fermentation |
Antioxidant Activity Comparison
Antioxidant activity tests have shown that green teas exhibit higher capacities compared to other types like orthodox or CTC teas. This correlates well with their higher total phenolic content.

Health Benefits Associated with High-Polyphenolic Green Tea Extracts
High-polyphenolic extracts from green tea have been associated with several potential health benefits:
- Cardiovascular Health Support: May help maintain heart health through antioxidant action.
- Anticancer Properties: Some studies suggest protective effects against certain cancers.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Could support cognitive function and neuroprotection.
These benefits are largely attributed to EGCG's potent antioxidant properties.
Cardiovascular Health Support
Research indicates that regular consumption of green tea may lower cholesterol levels and improve blood vessel function, thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. The polyphenols in green tea can help relax blood vessels, improving circulation and reducing blood pressure.
Anticancer Properties
Several studies have shown that EGCG can inhibit tumor growth and induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells. While more research is needed, preliminary findings suggest that green tea extracts may help reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, including breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers.
Neuroprotective Effects
The neuroprotective properties of green tea have garnered attention in recent years. Research suggests that EGCG may help protect neurons from damage and improve cognitive function. Some studies indicate that regular consumption could lower the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.
Weight Management
Green tea extracts are often included in weight loss supplements due to their potential ability to enhance fat oxidation and improve metabolic rates. Some studies suggest that EGCG may increase energy expenditure and fat burning during exercise.
Metabolic Health
Green tea has been linked to improved insulin sensitivity and reduced blood sugar levels, making it a beneficial beverage for individuals at risk of type 2 diabetes. The polyphenols in green tea may help regulate glucose metabolism, contributing to better overall metabolic health.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While generally safe when consumed moderately, high doses might interact negatively with certain medications or exacerbate conditions like anemia due to caffeine content. It's essential for individuals with specific health conditions or those taking medications to consult healthcare professionals before significantly increasing their intake of green tea extracts.
Conclusion
In summary, when it comes to achieving a high concentration of polyphenolics from green tea extracts, using optimal extraction techniques such as maceration with appropriate solvent compositions—like a 50% ethanol solution—is key. Additionally, understanding how different types compare helps appreciate why green remains one of the best sources among all varieties due both qualitatively & quantitatively superior profile over many counterparts.
The health benefits associated with high-polyphenolic green tea extracts make them an attractive addition to a balanced diet. However, it is essential to consume them mindfully and be aware of potential interactions with medications or health conditions.

Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions related to this topic:
1. What Are Polyhenolics?
- Polyphénolics refer broadly speaking towards any chemical compound containing multiple phenyl rings linked together via hydroxyl groups (-OH). They're naturally occurring substances often found within plant-based foods & beverages acting primarily as antioxidants helping protect cells against oxidative damage caused by free radicals.
2. How Do Extraction Methods Affect Yield?
- Different extraction methods such as maceration vs ultrasound assisted extractions influence yield because they vary efficiency levels extracting desired compounds without degrading them during process stages.
3. Why Is EGCG Important?
- Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) stands out among other catechins present within Camellia sinensis leaves mainly because it exhibits powerful anti-inflammatory & anti-cancerous activities making up roughly sixty percent total catechine composition contributing heavily toward beneficial bioactive effects observed upon consumption.
4. Can I Increase My Intake Safely?
- While moderate consumption generally poses no risks increasing intake should ideally occur under medical supervision especially if combining supplements alongside existing medications given potential interactions affecting efficacy safety profiles differently across individuals depending specific circumstances surrounding use patterns lifestyle habits etcetera
5. Does Steeping Time Matter?
- Yes! Steeping time impacts infusion strength including amounts released into liquid portion; longer steeping times release more solids including tannins potentially altering taste experience beyond just nutrient availability impacting perceived bitterness levels too!
Citations:
[1] https://jurnal.poltekkespim.ac.id/index.php/pharmademica/article/view/5
[2] https://www.nepjol.info/index.php/JFSTN/article/view/8264/6732
[3] https://www.mdpi.com/2306-5710/4/1/15
[4] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8430757/
[5] https://www.myfoodresearch.com/uploads/8/4/8/5/84855864/_1__fr-2017-117_shannon.pdf
[6] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8664505/
[7] https://deliveritpharmacy.com/shop/green-tea-70-high-concentration-egcg/
[8] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10542028/
[9] https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/sustainable-food-systems/articles/10.3389/fsufs.2023.1175893/pdf
[10] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8601035/






























