Content Menu
● Understanding Green Tea Extract
● Side Effects of Green Tea Extract
>> 1. Gastrointestinal Issues
>> 2. Liver Damage
>> 3. Caffeine-Related Side Effects
>> 4. Dizziness and Convulsions
>> 5. Interaction with Medications
● Safe Consumption Guidelines
● Additional Considerations
>> 1. Individual Variation
>> 2. Lifestyle Factors
>> 3. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What are the common side effects of green tea extract?
>> 2. How much green tea extract is considered safe?
>> 3. Can I drink green tea on an empty stomach?
>> 4. Is green tea extract safe for everyone?
>> 5. What should I do if I experience side effects from green tea extract?
● Citations:
Green tea extract has gained popularity as a dietary supplement due to its numerous health benefits, including weight loss, improved brain function, and antioxidant properties. However, excessive consumption can lead to adverse effects. This article explores the potential side effects of green tea extract, particularly focusing on how too much can make you sick.
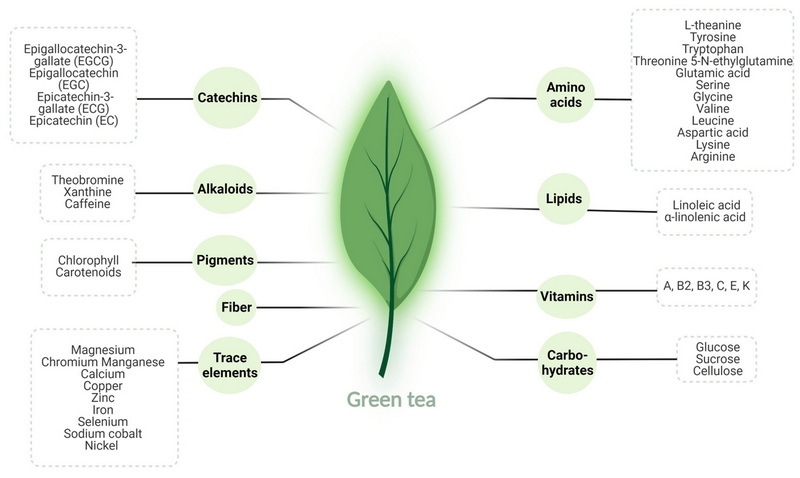
Understanding Green Tea Extract
What is Green Tea Extract?
Green tea extract is a concentrated form of green tea, derived from the leaves of the *Camellia sinensis* plant. It contains high levels of catechins, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which are responsible for many of its health benefits. Unlike regular green tea, which is brewed and consumed as a beverage, green tea extract is available in capsule, powder, or liquid form.
Health Benefits of Green Tea Extract
1. Antioxidant Properties: Green tea extract is rich in antioxidants that combat oxidative stress and inflammation. Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals in the body, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
2. Weight Loss: Studies suggest that it can aid weight loss by increasing fat oxidation and improving metabolic rate. Some research indicates that EGCG may enhance fat burning during exercise.
3. Heart Health: Regular consumption may lower cholesterol levels and improve heart health. It has been shown to reduce LDL cholesterol and triglycerides while increasing HDL cholesterol.
4. Brain Function: It has been linked to improved cognitive function and reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Some studies suggest that EGCG may protect neurons from damage and support overall brain health.
5. Diabetes Management: Green tea extract may help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity, making it beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Side Effects of Green Tea Extract
While green tea extract has various health benefits, excessive intake can lead to several side effects:
1. Gastrointestinal Issues
Excessive consumption of green tea extract can cause gastrointestinal problems such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These symptoms are often due to the high concentration of tannins in the extract, which can irritate the stomach lining.
People who consume green tea extract on an empty stomach are particularly susceptible to these side effects. The tannins can increase stomach acidity, leading to discomfort.
2. Liver Damage
One of the most serious concerns regarding high doses of green tea extract is its potential to cause liver damage. Studies have reported cases of hepatotoxicity associated with excessive intake of EGCG, particularly in supplement form. Symptoms of liver damage include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), fatigue, nausea, and abdominal pain.
In rare cases, acute liver failure has been linked to high doses of green tea extract supplements. It is crucial for consumers to be aware of their total daily intake from both supplements and dietary sources.
3. Caffeine-Related Side Effects
Green tea naturally contains caffeine, and consuming large amounts can lead to side effects such as insomnia, anxiety, irritability, and headaches. Individuals sensitive to caffeine may experience these symptoms even with moderate consumption.
The caffeine content in green tea extract varies by brand and formulation; thus, it's essential to check labels for caffeine content if you are sensitive or trying to limit your intake.
4. Dizziness and Convulsions
In rare cases, excessive intake of green tea extract has been linked to dizziness and convulsions. This is more likely to occur in individuals who consume high doses without proper medical supervision or those who have underlying health conditions that affect metabolism.
5. Interaction with Medications
Green tea extract can interact with certain medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness or increasing side effects. For example:
- Blood Thinners: Green tea may enhance the effects of anticoagulants like warfarin.
- Stimulants: The caffeine in green tea can amplify the effects of stimulant medications.
- Antidepressants: Some studies suggest that catechins may interfere with certain antidepressant medications.
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional before combining supplements with prescription drugs.

Safe Consumption Guidelines
To avoid adverse effects from green tea extract:
- Limit Intake: Do not exceed the recommended dosage on supplement labels or consume more than 4 cups of brewed green tea daily.
- Consult a Doctor: If you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking medications, consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
- Monitor Your Body's Response: Start with lower doses to assess tolerance before gradually increasing.
- Choose Quality Products: Opt for reputable brands that provide clear information about their products' contents and dosages.
Additional Considerations
1. Individual Variation
It's important to recognize that individuals may respond differently to green tea extract based on factors such as genetics, existing health conditions, and overall diet. Some people may tolerate higher doses without issues while others may experience side effects at lower amounts.
2. Lifestyle Factors
Incorporating green tea extract into a balanced lifestyle that includes a healthy diet and regular exercise can enhance its benefits while minimizing risks. Relying solely on supplements for weight loss or health improvements is not advisable.
3. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should exercise caution when considering green tea extract due to its caffeine content and potential effects on fetal development or infant health.
Conclusion
While green tea extract offers numerous health benefits, it is crucial to consume it responsibly. Excessive intake can lead to serious health issues such as gastrointestinal problems and liver damage. Always consult healthcare professionals when considering dietary supplements.

FAQ
1. What are the common side effects of green tea extract?
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headaches, and liver issues when consumed in excess.
2. How much green tea extract is considered safe?
Moderate consumption is generally safe; however, it's advisable not to exceed 800 mg of EGCG per day from supplements.
3. Can I drink green tea on an empty stomach?
Drinking green tea on an empty stomach may increase the likelihood of gastrointestinal discomfort due to its tannin content.
4. Is green tea extract safe for everyone?
While many people can safely consume green tea extract, those with liver conditions or caffeine sensitivity should exercise caution.
5. What should I do if I experience side effects from green tea extract?
If you experience any adverse effects after consuming green tea extract, discontinue use immediately and consult a healthcare provider.
Citations:
[1] https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=19&contentid=greenteaextract
[2] https://senchateabar.com/blogs/blog/green-tea-side-effects
[3] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-J4uzMyRRDY
[4] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-benefits-of-green-tea-extract
[5] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7009618/
[6] https://www.vumc.org/poison-control/toxicology-question-week/march-12-2021-what-are-adverse-effects-green-tea-extract
[7] https://www.shape.com/healthy-eating/healthy-drinks/too-much-green-tea-or-matcha-could-lead-liver-damage
[8] https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-960/green-tea
[9] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/269538






























