Content Menu
● Nutritional Profile of Green Tea Extract
>> Carbohydrate Content
● Health Benefits of Green Tea Extract
● How Green Tea Extract Works
>> Catechins
>> Caffeine
● Detailed Health Benefits
>> 1. Weight Management
>> 2. Cardiovascular Health
>> 3. Antioxidant Effects
>> 4. Blood Sugar Control
>> 5. Cognitive Function
● Potential Side Effects and Considerations
● Recommended Dosage
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. Is there any carbohydrate in green tea?
>> 2. Can green tea extract aid in weight loss?
>> 3. Are there any side effects associated with green tea extract?
>> 4. How should I take green tea extract for best results?
>> 5. Can I drink regular green tea instead of taking supplements?
● Citations:
Green tea extract is a concentrated form of green tea derived from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant. It has gained popularity due to its numerous health benefits, including weight management, improved metabolism, and enhanced overall health. One common question that arises is whether green tea extract contains carbohydrates.
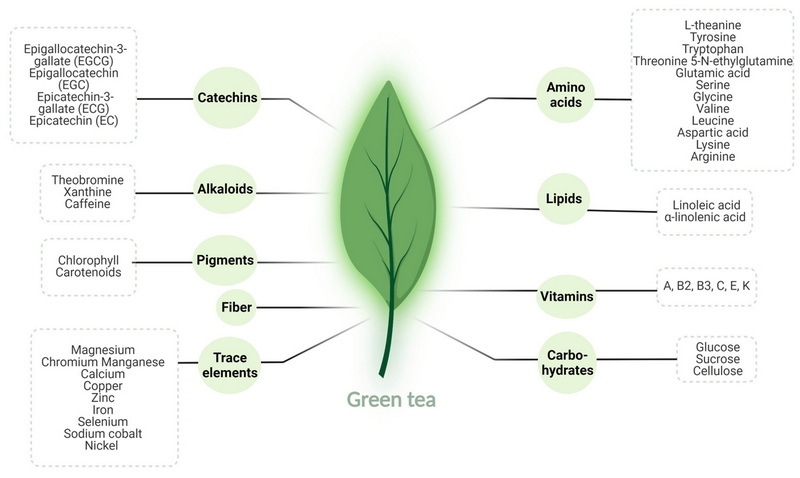
Nutritional Profile of Green Tea Extract
When examining the nutritional composition of green tea extract, it is essential to note that it is typically available in capsule, powder, or liquid form. The key components of green tea extract include:
- Catechins: These are powerful antioxidants that help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the body.
- Caffeine: Green tea extract contains caffeine, which can boost energy levels and enhance metabolic rate.
- Other Nutrients: While green tea leaves contain various vitamins and minerals, the extraction process concentrates specific compounds like catechins and caffeine.
Carbohydrate Content
According to multiple sources, green tea extract contains 0 grams of carbohydrates per serving. For instance:
- A capsule of green tea extract typically has 0g total carbs and 0g net carbs.
- This means that whether you consume it in capsule form or as a powder mixed with water or other beverages, you will not be adding any carbohydrates to your diet.
Health Benefits of Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract is renowned for its potential health benefits, which include:
- Weight Loss Support: The catechins in green tea extract may enhance fat oxidation and improve metabolic rate, aiding in weight loss efforts.
- Antioxidant Properties: The high concentration of antioxidants helps combat oxidative stress and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Heart Health: Regular consumption of green tea extract has been linked to improved cardiovascular health by lowering cholesterol levels and improving blood circulation.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Some studies suggest that green tea extract can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
How Green Tea Extract Works
The effectiveness of green tea extract can be attributed to its active compounds:
Catechins
The most significant catechin found in green tea extract is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). Research indicates that EGCG can inhibit enzymes responsible for carbohydrate digestion, such as alpha-amylase. This inhibition may lead to reduced absorption of dietary starches and sugars.
Caffeine
Caffeine also plays a role in enhancing metabolic rate and promoting fat oxidation. It works synergistically with catechins to maximize fat-burning effects during exercise.

Detailed Health Benefits
1. Weight Management
Green tea extract has been extensively studied for its role in weight management. Several meta-analyses have shown that it can significantly reduce body weight and body mass index (BMI). For example, a study involving overweight individuals demonstrated that those who consumed 400–500 mg of green tea extract daily experienced notable reductions in body fat percentage compared to those who did not take the supplement[1][2].
2. Cardiovascular Health
The catechins found in green tea extract have been shown to improve heart health by reducing LDL cholesterol levels and triglycerides. In one study, participants who took 379 mg of green tea extract daily for three months showed significant improvements in their lipid profiles[3][4]. This reduction in cholesterol levels can decrease the risk of heart disease and stroke.
3. Antioxidant Effects
Green tea extract is rich in antioxidants, particularly EGCG, which has been shown to protect cells from oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is linked to various chronic diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders[5][6]. By neutralizing free radicals, the antioxidants in green tea extract may help prevent cellular damage.
4. Blood Sugar Control
Research indicates that green tea extract can help regulate blood sugar levels. A systematic review found that individuals with type 2 diabetes who took green tea supplements experienced lower fasting blood sugar levels and improved insulin sensitivity[7][8]. This effect may be beneficial for managing diabetes and reducing the risk of complications associated with the condition.
5. Cognitive Function
Emerging evidence suggests that the consumption of green tea extract may enhance cognitive function and protect against neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Studies have shown that EGCG can improve memory and cognitive performance by increasing blood flow to the brain[9][10].
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
While green tea extract is generally safe for most people when consumed in moderation, excessive intake can lead to adverse effects such as:
- Liver Damage: High doses of green tea extract have been associated with liver toxicity in some individuals[11][12]. Symptoms may include nausea, stomach pain, yellowing of the skin or eyes, and dark urine.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Some users may experience stomach upset or nausea when taking green tea extract on an empty stomach[13].
- Interactions with Medications: Green tea extract may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners and medications for anxiety or depression[14].
Recommended Dosage
The optimal dosage for green tea extract varies depending on individual health goals:
- For weight loss: A daily intake of 400–500 mg EGCG equivalent has been shown to be effective.
- For cardiovascular health: Consuming around 379 mg daily has demonstrated improvements in cholesterol levels.
- For cognitive enhancement: A dosage between 336 mg to 1,440 mg per day has been suggested based on various studies[15][16].
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Conclusion
In summary, green tea extract does not contain any carbohydrates. It is a low-calorie supplement packed with antioxidants that can provide various health benefits, including weight management, improved heart health, better blood sugar control, and enhanced cognitive function. However, it is essential to consume it responsibly and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.

FAQ
1. Is there any carbohydrate in green tea?
No, green tea extract contains 0 grams of carbohydrates per serving.
2. Can green tea extract aid in weight loss?
Yes, studies suggest that the catechins in green tea extract can enhance fat oxidation and improve metabolic rate.
3. Are there any side effects associated with green tea extract?
While generally safe in moderation, excessive intake can lead to liver damage and gastrointestinal issues.
4. How should I take green tea extract for best results?
It is recommended to take green tea extract with food to minimize potential gastrointestinal discomfort.
5. Can I drink regular green tea instead of taking supplements?
Yes, drinking regular brewed green tea can provide similar benefits as taking supplements but may require consuming multiple cups to achieve comparable amounts of catechins.
Citations:
[1] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-benefits-of-green-tea-extract
[2] https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=19&contentid=greenteaextract
[3] https://www.eatthismuch.com/calories/green-tea-extract-1659251
[4] https://www.rxlist.com/green_tea/generic-drug.htm
[5] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38031409/
[6] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6412948/
[7] https://www.vumc.org/poison-control/toxicology-question-week/march-12-2021-what-are-adverse-effects-green-tea-extract
[8] https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/nutrition/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022.1084455/full
[9] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2855614/
[10] https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-76714/green-tea-leaf-extract-oral/details
[11] https://www.carbmanager.com/food-detail/md:c3e7e12c9fcfba3df6dfd85868050459/green-tea-extract
[12] https://examine.com/supplements/green-tea-extract/
[13] https://ajcn.nutrition.org/article/S0002-9165(22)04202-2/fulltext
[14] https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/herb/green-tea
[15] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3746392/
[16] https://www.webmd.com/diet/health-benefits-green-tea
[17] https://www.drugs.com/npp/green-tea.html
[18] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/269538
[19] https://medsafe.govt.nz/profs/PUArticles/Complementary%20Medicine%20Corner%20-%20Safety%20of%20Green%20Tea%20extracts.htm
[20] https://consensus.app/questions/much-green-take-daily/
[21] https://health.clevelandclinic.org/green-tea-extract-a-better-way-to-boost-energy-or-not
[22] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7009618/
[23] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/egcg-epigallocatechin-gallate
[24] https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-960/green-tea
[25] https://www.vitalnutrients.co/products/green-tea-extract
[26] https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/food-nutrition/public-involvement-partnerships/notice-modification-list-permitted-supplemental-ingredients-permit-use-green-tea-extract-supplemental-ingredient-foods/document.html






























